Indigenous peoples and their allies have intensified their fight against two oil companies over contamination in the Peruvian Amazon. Last week, a group of indigenous protesters blockaded portions of the Marañon and Corrientes Rivers in the province of Loreto in northeastern Peru. The protesters were demanding that Pluspetrol, an Argentinean oil company, compensate them for a recent oil spill. As of December 28th, after eight days, the blockade remained unbroken.
This follows on the heels of a similar blockade in October, which drew five thousand indigenous protesters from the Achuar, Awajun and Shawi tribes. That blockade, which lasted for weeks, ended only when the regional government finally agreed to perform water quality tests in the Marañon.
Right now, the main issue is contamination from an oil spill in June 2010, when 400 barrels of oil spilled into the Marañon from a tanker transporting oil for Pluspetrol. The company has blamed outside contractors for the accident, but indigenous groups are still demanding that Pluspetrol pay up. They are asking the company to undertake reforestation efforts in degraded areas, in addition to providing food, medicines, and cash payments to affected communities.
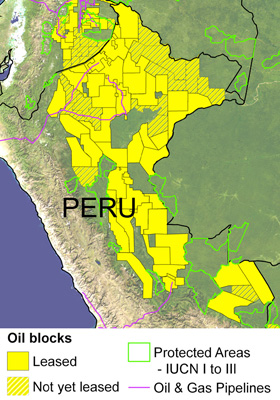 Oil and gas blocks in the western Amazon. Solid yellow indicates blocks already leased out to companies. Hashed yellow indicates proposed blocks or blocks still in the negotiation phase. Protected areas shown are those considered strictly protected by the IUCN (categories I to III). Image modified from Finer M, Jenkins CN, Pimm SL, Keane B, Ross C, 2008 Oil and Gas Projects in the Western Amazon: Threats to Wilderness, Biodiversity, and Indigenous Peoples. PLoS ONE 3(8): e2932. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002932 |
The battle over the oil spill is only the latest installment in a much longer fight. Pluspetrol owns two oil concessions in this part of the Peruvian Amazon, known as Blocks 1AB and 8. The two blocks have been producing oil for decades; for most of that time, toxic residues have been dumped in rivers or left in open pits. Heavy metals, volatile organic compounds, and hydrocarbons have infiltrated water supplies, sickening local residents. For years, the Achuar tribe, which inhabits the area, has been fighting for compensation and clean up.
Pluspetrol has only owned the blocks since 2000. The previous owner, Occidental, was responsible for most of the pollution. The Achuar have been fighting Occidental in court since 2007. On December 8th, they scored a major victory when a judge in Los Angeles ruled that their class action lawsuit could be heard in the US, as opposed to Peru. The change of venue makes it much more likely that the lawsuit will be successful.
Still, it is not clear that all will end well. Previous blockades by indigenous groups have ended in violence. In June 2009, in another part of the Peruvian Amazon, indigenous groups created blockades over roads to protest new oil and gas concessions. The protests led to bloody confrontations with the police. At least 20 policemen and 34 protesters were ultimately killed, with many more reported missing.
Oil production in Peru has expanded rapidly over the past five years, and today 41% of the percent of the Peruvian Amazon is currently covered by oil and gas concessions [PDF]. Blocks 1AB and 8, which together produce around 30,000 barrels of oil a day, are responsible for approximately 40% of Peru’s overall oil production.
Full disclosure: I recently worked as an intern for Amazon Watch, including some work on a campaign against Pluspetrol.
Related articles
50 NGOS tell big oil to get out of uncontacted natives’ territory
(11/21/2010) A letter signed by over 50 NGOs is calling on three big oil companies—Perenco, Repsol-YPF, and ConocoPhillips—to withdraw from Peruvian territory inhabited by uncontacted indigenous tribes. The letter states that the oil companies’ presence in the area threatens the uncontacted tribe with diseases, for which they have little immunity, and puts the lives of oil company workers in jeopardy, since past encounters have ended in violence.
NGO warns oil exploration in Peru may ‘decimate’ uncontacted tribes
(10/17/2010) Survival International has warned that oil exploration in northern Peru threatens two uncontacted tribes. The organization, devoted to indigenous rights, has sent a letter to the UN’s Special Rapporteur on indigenous peoples, James Anaya, alleging that Peru is “violating international law” by allowing oil companies to explore a region home to uncontacted people, who are especially vulnerable to disease.
Peru’s rainforest highway triggers surge in deforestation, according to new 3D forest mapping
(09/06/2010) Scientists using a combination of satellite imagery, airborne-laser technology, and ground-based plot surveys to create three-dimensional high resolution carbon maps of the Amazon rainforest have documented a surge in emissions from deforestation and selective logging following the paving of the Trans-Oceanic Highway in Peru. The study, published this week in the early edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, reveals that selective logging and other forms of forest degradation in Peru account for nearly a third of emissions compared to deforestation alone.
(05/24/2010) Perupetro, the Peruvian government’s oil and gas corporate leasing body, announced last week that it will open an additional 25 lots for oil and gas exploration in the Amazon covering an area of 10 million hectares (nearly 25 million acres). Peru’s national Amazon indigenous group, AIDESEP, criticized the move calling it a ‘new threat’ to Peru’s indigenous group. According to Amazon Watch these new lots mean that 75 percent of the Peruvian Amazon is now open to oil and gas exploration and drilling.
Oil company to cut 454 kilometers of seismic lines in uncontacted tribe territory
(04/21/2010) Repsol YPF, a Spanish-Argentine oil company, plans to cut 454 kilometers (282 miles) of seismic lines in a territory of the Peruvian rainforest known to be home to uncontacted indigenous peoples, according to a press release from Survival International. To construct seismic lines paths will be cleared in the forest and explosives set-off regularly. Seismic lines allow energy companies to locate oil deposits by creating a cross sectional view of the subsurface.
Spanish oil company develops own rules for contacting uncontacted Amazon tribes

(03/26/2010) Imagine you’re in one of the remotest parts of the Amazon rainforest and suddenly you come across members of an uncontacted tribe. What should you do? The experts say, “Turn around. At all costs, make no attempt at contact.” Repsol YPF, exploring for oil in northern Peru, has taken a different approach. Despite the extreme vulnerability of the tribes to any form of contact, the company suggests that its workers talk to them in certain instances, and even provides specific phrases to use and conversation topics to address.
Under siege: oil and gas concessions cover 41 percent of the Peruvian Amazon

(02/16/2010) A new study in the Environmental Research Letter finds that the Peruvian Amazon is being overrun by the oil and gas industries. According to the study 41 percent of the Peruvian Amazon is currently covered by 52 separate oil and gas concessions, nearly six times as much land as was covered in 2003. “We found that more of the Peruvian Amazon has recently been leased to oil and gas companies than at any other time on record,” explained co-author Dr. Matt Finer of the Washington DC-based Save America’s Forests in a press release. The concessions even surpass the oil boom in the region during the 1970s and 80s, which resulted in extensive environmental damage.

(12/22/2009) In James Cameron’s newest film Avatar an alien tribe on a distant planet fights to save their forest home from human invaders bent on mining the planet. The mining company has brought in ex-marines for ‘security’ and will stop at nothing, not even genocide, to secure profits for its shareholders. While Cameron’s film takes place on a planet sporting six-legged rhinos and massive flying lizards, the struggle between corporations and indigenous people is hardly science fiction.
Amazonian natives say they will defend tribal lands from Hunt Oil with “their lives”

(10/25/2009) Indigenous natives in the Amazon are headed to the town of Salvacion in Peru with a plan to forcibly remove the Texas-based Hunt Oil company from their land as early as today. Peruvian police forces, numbering in the hundreds, are said to be waiting in the town. The crisis has risen over an area known as Lot 76, or the Amarakaeri Communal Reserve. The 400,000 hectare reserve was created in 2002 to protect the flora and fauna of the area, as well as to safeguard watersheds of particular importance to indigenous groups in the region.
Heavy oil pollution remains in Amazon, despite company claiming clean-up is finished
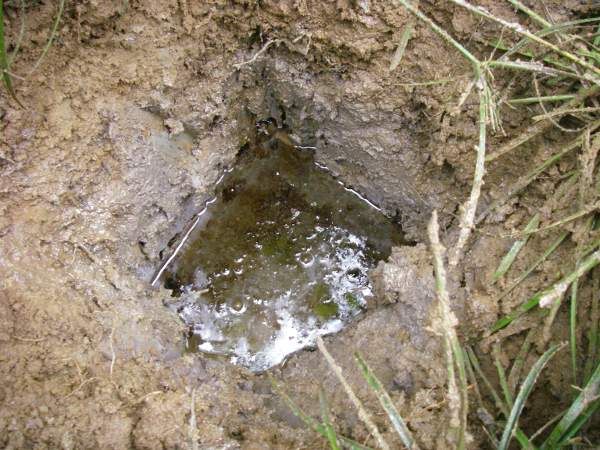

(09/17/2009) A new report shows that the Corrientes region of the Peruvian Amazon, which suffered decades of toxic contamination by Occidental Petroleum (OXY), is far from being cleaned-up. The survey, conducted by US non-profit E-Tech International, found that heavy metals, volatile organic compounds, and hydrocarbons still exist at levels above the safety limits set by Peru and continue to threaten the Achuar indigenous community, who have long fought against the oil companies.
Police face murder charges in killing of indigenous protesters in Peru
(08/16/2009) A federal prosecutor in Peru filed murder charges against two police generals and 15 other officers over the deaths of indigenous protesters at a roadblock in June, reports the Associated Press. The Indians were protesting new rules that would have made it easier for foreign developers to exploit oil and gas, timber, and minerals in Peru’s Amazon rainforest. The skirmish left 23 police and at least ten protesters dead.
Peru to proceed with oil and gas auctions in the Amazon despite indigenous protests
(08/07/2009) Despite violent protests by indigenous groups over plans to expand oil and gas exploration in the Peru’s Amazon rainforest, energy investments in the South American country are expected to increase to $1.5 billion in both 2009 and 2010, reports Reuters.













