Voluntary carbon markets greatly expanded in both transaction volume and value in 2008, providing critical funds for projects aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, according to a new report from Ecosystem Marketplace and New Carbon Finance.
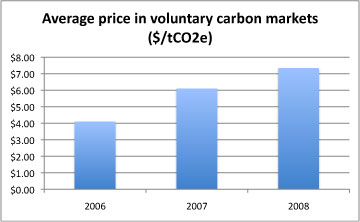
Fortifying the Foundation: State of the Voluntary Carbon Markets 2009 — a survey of over 190 voluntary carbon credit retailers, brokers, accounting registries, and exchanges — found that voluntary carbon markets transacted 123 million metric tons of carbon credits valued at $705 million in 2008, up from 65 million tons of credits valued at $331 million in 2007. The average price for voluntary offset credits increased 20 percent from $6.10 to $7.34 per ton of carbon dioxide.
“With cap and trade expanding globally, the voluntary markets are starting to play a crucial role in project development and capacity building as companies start to prepare for emission caps. At the same time, the continued prominence of European demand ensures that the voluntary markets also have a unique role to play alongside compliance markets,” said Milo Sjardin, Head of North America for New Carbon Finance and coauthor of the report.
|
State of the Voluntary Carbon Markets 2009 found that while corporate social responsibility and public relations benefits are the most common motivations for buying voluntary offsets, some customers are purchasing offsets as investments in anticipation of higher prices in voluntary markets and the possible emergence of compliance markets.
“Over the past three years, we have witnessed this market grow rapidly in volume and maturity. The 2008 markets saw further establishment of offset standards and the initial integration of registries, while continuing to serve as an incubation space for project types not currently accepted in the Kyoto markets,” said Katherine Hamilton, Managing Director of Ecosystem Marketplace and coauthor of the report.
Asia was the largest source of offsets for voluntary markets, accounting for 45 percent of all carbon credits bought on the OTC market in 2008.
More than half of carbon offsets came from renewable energy projects. Landfill gas (methane) projects were the second most popular source of offsets, accounting for about one sixth of the market.
The report found 96 percent of offset credits were verified to a third party standard in 2008. Leading verification standards were the Voluntary Carbon Standard, the Gold Standard, the Climate Action Reserve, and the American Carbon Registry.
State of the Voluntary Carbon Markets 2009 is available at Ecosystem Marketplace














