45% chance Gulf Stream current will collapse by 2100 finds research
Rhett A. Butler, mongabay.com
December 7, 2005
New research indicates there is a 45 percent chance that the thermohaline circulation in the North Atlantic Ocean could shut down by the end of the century if nothing is done to slow greenhouse gas emissions.
Even with immediate climate policy action, say scientists, there would still be a 25 percent probability of a collapse of the system of currents that keep western Europe warmer than regions at similar latitudes in other parts of the world.
The Atlantic thermohaline circulation, better known as the Atlantic heat conveyor belt, is a system of currents in the Atlantic Ocean that result in a net transport of warm water into the northern hemisphere. A weakening of the system, which includes the Gulf Stream, could cause a cooling in northwest Europe and worsen droughts in equatorial Africa.
The research will be presented by Michael Schlesinger, a professor of atmospheric sciences at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, tomorrow at the United Nations Climate Control Conference in Montreal.
“We found that there is a 70 percent likelihood of a thermohaline collapse, absent any climate policy,” Schlesinger said in a statement, “Although this likelihood can be reduced by the policy intervention, it still exceeds 25 percent even with maximal policy intervention.” Because the risk of a thermohaline collapse is unacceptably large, Schlesinger believes carbon capture and sequestration should be given serious consideration in addition to the policy measures — like carbon taxes — currently on the table.
A news release announcing the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign research, appears below.
Global warming could halt ocean circulation, with harmful results
By James E. Kloeppel, Physical Sciences Editor
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
12/6/05
Absent any climate policy, scientists have found a 70 percent chance of shutting down the thermohaline circulation in the North Atlantic Ocean over the next 200 years, with a 45 percent probability of this occurring in this century. The likelihood decreases with mitigation, but even the most rigorous immediate climate policy would still leave a 25 percent chance of a thermohaline collapse.
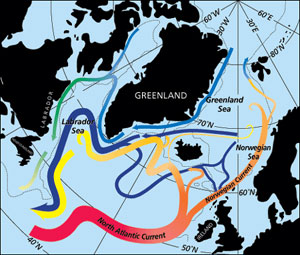 The North Atlantic Current Pathways associated with the transformation of warm subtropical waters into colder subpolar and polar waters in the northern North Atlantic. Along the subpolar gyre pathway the red to yellow transition indicates the cooling to Labrador Sea Water, which flows back to the subtropical gyre in the west as an intermediate depth current (yellow). More information |
“This is a dangerous, human-induced climate change,” said Michael Schlesinger, a professor of atmospheric sciences at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. “The shutdown of the thermohaline circulation has been characterized as a high-consequence, low-probability event. Our analysis, including the uncertainties in the problem, indicates it is a high-consequence, high-probability event.”
Schlesinger will present a talk “Assessing the Risk of a Collapse of the Atlantic Thermohaline Circulation” on Dec. 8 at the United Nations Climate Control Conference in Montreal. He will discuss recent work he and his colleagues performed on simulating and understanding the thermohaline circulation in the North Atlantic Ocean.
The thermohaline circulation is driven by differences in seawater density, caused by temperature and salinity. Like a great conveyor belt, the circulation pattern moves warm surface water from the southern hemisphere toward the North Pole. Between Greenland and Norway, the water cools, sinks into the deep ocean, and begins flowing back to the south.
 Michael Schlesinger Atmospheric sciences professor Michael Schlesinger says global warming could halt ocean circulation. “This is a dangerous, human-induced climate change,” he said. Photo courtesy of the University of Illinios. |
“This movement carries a tremendous amount of heat northward, and plays a vital role in maintaining the current climate,” Schlesinger said. “If the thermohaline circulation shut down, the southern hemisphere would become warmer and the northern hemisphere would become colder. The heavily populated regions of eastern North America and western Europe would experience a significant shift in climate.”
Higher temperatures caused by global warming could add fresh water to the northern North Atlantic by increasing the precipitation and by melting nearby sea ice, mountain glaciers and the Greenland ice sheet. This influx of fresh water could reduce the surface salinity and density, leading to a shutdown of the thermohaline circulation.
“We already have evidence dating back to 1965 that shows a drop in salinity around the North Atlantic,” Schlesinger said. “The change is small, compared to what our model needs to shut down the thermohaline, but we could be standing at the brink of an abrupt and irreversible climate change.”
To analyze the problem, Schlesinger and his colleagues first used an uncoupled ocean general circulation model and a coupled atmosphere-ocean general circulation model to simulate the present-day thermohaline circulation and explore how it would behave in response to the addition of fresh water.
|
Related Climate News
Tropical Atlantic cooling and deforestation correlate to drought in Africa Against the backdrop of the Montreal Summit on global climate being held this week, an article on African droughts and monsoons, by a University of California, Santa Barbara scientist and others, which appears in the December issue of the journal Geology, underlines concern about the effects of global climate change. Change in Atlantic circulation could plunge Europe into cold winters The Atlantic Ocean circulation that carries warm waters north and returns cold waters south is slowing, putting Europe at risk of colder temperatures, according to research published in Nature. The Atlantic Heat Conveyor, the system of currents in the Atlantic Ocean that result in a net transport of warm water into the northern hemisphere, keeps western Europe warmer than regions at similar latitudes in other parts of the world. A weakening of the system, which includes the Gulf Stream, could cause a cooling in northwest Europe. Below are two news releases, one from the University of Southampton detailing the current study, and an earlier one from NASA looking at the slowing of currents in the Atlantic. |
They then used an extended, but simplified, model to represent the wide range of behavior of the thermohaline circulation. By combining the simple model with an economic model, they could estimate the likelihood of a shutdown between now and 2205, both with and without the policy intervention of a carbon tax on fossil fuels. The carbon tax started out at $10 per ton of carbon (about five cents per gallon of gasoline) and gradually increased.
“We found that there is a 70 percent likelihood of a thermohaline collapse, absent any climate policy,” Schlesinger said. “Although this likelihood can be reduced by the policy intervention, it still exceeds 25 percent even with maximal policy intervention.”
Because the risk of a thermohaline collapse is unacceptably large, Schlesinger said, “measures over and above the policy intervention of a carbon tax — such as carbon capture and sequestration — should be given serious consideration.”
Collaborators on this research are U. of I. research programmer Bin Li, Princeton University researchers Sergey Malyshev and Jianjun Yin, University of Michigan research scientist Natasha Andronova, and Wesleyan University economics professor Gary Yohe.
The National Science Foundation funded the work.
This story includes a modified news release titled “Global warming could halt ocean circulation, with harmful results” from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.







