This article—written in April 2010, updated in August 2010, and posted for the first time today—is part of larger “Fate of Forests” series.
The commercial shows a typical office setting. A worker sits drearily at a desk, shredding papers and watching minutes tick by on the clock. When his break comes, he takes out a Nestle KitKat bar. As he tears into the package, the viewer, but not the office worker, notices something is amiss—what should be chocolate has been replaced by the dark hairy finger of an orangutan. With the jarring crunch of teeth breaking through bone, the worker bites into the “bar.” Drops of blood fall on the keyboard and run down his face. His officemates stare, horrified. The advertisement cuts to a solitary tree standing amid a deforested landscape. A chainsaw whines. The message: Palm oil—an ingredient in many Nestle products—is killing orangutans by destroying their habitat, the rainforests of Borneo and Sumatra.
The advertisement ran under Greenpeace’s campaign to pressure the world’s largest food processor to switch from an allegedly damaging palm oil supplier. Nestle’s response—censoring the ad citing copyright infringement—brought the campaign worldwide attention and dredged up some dark episodes from Nestle’s past, eventually forcing the company to backtrack and engage in extensive damage control. Nestle dumped its supplier—Sinar Mas—shortly thereafter and implemented new policies to ensure that the palm oil it uses would never again be linked to rainforest destruction. The campaign—and Nestle’s disastrous response, followed by capitulation—illustrates the leverage activists have in pressuring big corporations on their environmental performance.
Oil palm plantations in Sabah, Malaysia. The palm oil industry maintains its product is “greening the planet” but the reality is more complex
Palm oil, usually produced from a species of palm tree originally from West Africa, has emerged over the past 30 years as one of the world’s most widely used—and controversial—crops. Palm oil goes into a range of products available in virtually every supermarket, pharmacy, and department store. It is used in roughly half of processed foods, ranging from crackers to peanut butter to ice cream; beauty products like shampoo, cosmetics, shaving cream, and soap (which account for nearly 10 percent of global consumption of palm oil); industrial lubricants; and even for biofuel production. Its versatility, combined with a yield far in excess of any other oilseed, has fueled its rapid expansion across southeast Asia: today, Indonesia and Malaysia—which account for 85 percent of global palm oil production—have more than 50,000 square miles of palm plantations, up from fewer than 580 square miles in 1984. But the crop’s success has come at a great environmental cost: more than half of the expansion since 1980 has come at the expense of natural forests. As such, palm oil has been targeted by environmentalists and scientists concerned about biodiversity loss, greenhouse gas emissions, and pollution. Furthermore, the palm oil industry has been challenged by land rights issues and social abuses, since expansion is occurring in areas where communities may traditionally use forests but lack title to land. New development in these areas spurs charges of land-grabbing and can exacerbate social conflict.
Rainforest to Plantation
|
|
The palm oil industry is one where economies of scale are critical to commercial viability. As such, plantations tend to be large—a minimum of 4,000 hectares (10,000 acres) of oil palm is needed to supply a single palm oil mill, although most plantations are bigger. The need to secure large blocks of land in Malaysia and Indonesia have led developers to run roughshod over traditional forms of land tenure, many of which are informal or customary rather than secured by a formal legal process. According to surveys conducted by the Forest Peoples Programme, a UK-based indigenous rights organization, and the Environmental Investigative Agency (EIA), an international environmental group, land is often sold or long-term leased to plantations companies without the knowledge or consent of local communities. Often it is a single local official who signs off the agreement—an opportunity ripe for corruption, especially in villages where the “gift” of a simple motorbike can win substantial influence, including a land contract. But in even when permission is sought, local landowners may not be clearly informed of the terms of the contact or understand they are signing away rights to their land for 30 years or longer. In its investigation into dealings in West Papua on the island of New Guinea, EIA found a case in where a four-year-old was required to sign a contract—using a thumbprint, since he couldn’t write his own name—to ensure the plantation would remain under company rule for decades. The company—which paid less than $3 per hectare for a 25-year lease to the land—proceeded to clear more forest than agreed and chopped down a small forest area the child’s family had requested be left standing to meet their day-to-day needs. But such practices should perhaps come as little surprise given the preference for development projects over customary tenure under Indonesian law. A report published in 2005 by the World Agroforestry Centre found that less than 0.2 percent of Indonesia’s land territory classified as forest (70 percent of Indonesia’s total land mass) has been allocated to communities under legal tenure. Commercial forestry concessions represented the bulk of land permits.
But the social problems don’t end even in places where communities do own their land and willingly sign up to grow oil palm. The financial arrangements of smallholder systems—whereby a group of small growers sell their product to a mill for processing—are subject to abuse and can lock producers in a cycle of debt as they pay for seedlings, fertilizer, and pesticides. The perishability of palm oil—fruit much be processed within 48 hours of harvesting—and contractual obligations, makes it impossible for a smallholder to sell his product elsewhere. The price received is set by the mill.
Once rights to establish a plantation are secured, converting rainforest into oil palm plantation is not an easy undertaking. Generally, valuable timber—derived from towering meranti, ramin, and merbau trees—is logged and sold to a mill usually for conversion into veneers for furniture or flooring, while less valuable trees are fed into a pulper, converting decades of life into a raw material for paper production. The remaining vegetation is burned—sometimes with devastating impacts on surrounding forest areas. If the land is swampy, it is drained and then planted with palm seedlings. To maximize efficiency of harvesting, trees are densely planted in neat rows as a monoculture. Within three years these seedlings produce their first bounty of red-orange fruit bunches. Each bunch, weighing up to 100 pounds, is harvested by hand and taken by truck to a milling facility where it is primarily converted into palm oil, a bright orange liquid in its raw form. The oil is processed and shipped to towns, cities, and ports. Much of it ends up overseas: in 2008 palm oil exports from Indonesia and Malaysia exceeded $30 billion, the bulk of which went to India and China, followed by Bangladesh, the Netherlands, Germany, and the United States. Some of the world’s largest consumer products companies—like Nestle, Unilever, General Mills, Kraft, and Proctor & Gamble—are also among the biggest Western buyers of palm oil.
 Oil palm plantation reëstablished on former rainforest land in North Sumatra. The elephant in the room for Malaysia and Indonesia is what happens should Brazil make good on its goal to establish 5 million hectares of oil palm plantations on long-ago deforested lands? Will the potentially huge influx of certified-sustainable palm oil effectively shut palm oil with questionable origins out of the most lucrative consumer markets? Will the new production reduce palm oil prices? |
Producing palm oil on rainforest lands or peat swamp has a staggering environmental impact. Converting virgin rainforest, which may store more than 400 tons of carbon per hectare, to an oil palm plantation that stores less than 40 tons of carbon per hectare over its 25-year-life results in substantial greenhouse gas emissions, but conversion of peatlands—swampy wetlands that store immense amounts of carbon in their soils, but release it when exposed to air—is even worse. A 2007 study by Susan Page of the University of Leicester found that one ton of palm oil produced on peatland generates 15 to 70 tons of carbon dioxide, largely the result of deforestation and draining of peatlands, making palm oil-based-biofuels produced by peatlands conversion worse for climate than burning of conventional fossil fuels. In 2008, policy makers in Europe seeking to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the transport sector by importing biofuels from Malaysia and Indonesia were shocked when lifecycle analyses showed it can take more than 400 years for biodiesel produced from palm oil grown on peatlands to show emissions savings relative to regular diesel. Oil palm plantations are in production an average of 25 years, rendering the potential savings a moot point.
Still worse, greenhouse gas emissions are exacerbated by fire. Dry peatlands are highly combustible and once ignited, can burn for years, causing air pollution. In particularly dry years, peat fires cast a pall over Malaysia, Singapore, and Thailand, triggering health warnings, transportation headaches, and political discord. At the peak of the 1997-1998 fires—set mostly for land-clearing in Borneo and Sumatra—simply breathing the air in Singapore or Kuala Lumpur was equivalent to smoking three packs of cigarettes a day. All told some 5.2 million hectares or nearly 13 million acres went up in flames during that episode.
Severe fires now return on nearly an annual basis. In 2005 fires in Indonesia drove the air pollution index to 500 for the first time in peninsular Malaysia, a level at which people are advised to avoid all physical activity outdoors and people with heart or lung disease, adults over 45 years, and children are urged to remain indoors and keep activity levels to a minimum. Indignant politicians in Singapore and Malaysia blasted Indonesia, which coyly responded that the bulk of the fires were burning in forest concessions controlled by Malaysian and Singaporean plantation companies. Malaysia’s prime minister called on mosque-goers to pray for rain.
But the environmental impacts of oil palm aren’t limited to humans: expansion has taken a toll on some of Asia’s rarest—and most charismatic—species, including Sumatran rhinos and tigers, Borneo pygmy elephants, small cats, and the beloved red ape: the orangutan. Biologists now say that palm oil consumption is the greatest threat to the greatest number of species.

Oil palm and logged over rainforest in Sabah, Malaysia. Photo by Rhett A. Butler 2008.
Compared to even heavily logged natural forest, an oil palm plantation is a biological desert. The monotony of monoculture allows a small number of species—including palm civets, rats, and leopard cats—to proliferate, but forces the great majority of rainforest species—over 80 percent compared to untouched forest—to seek habitat elsewhere or perish. The reason? Conversion to oil palm eliminates entire niches in the forest, destroying the canopy, annihilating complex nutrient cycling systems, and turning clear-flowing streams into squalid repositories of fertilizers, pesticides, and industrial chemicals. Species like the fishing cat and the flat-headed cat—so rare that Jim Sanderson, the world’s leading small cat expert, has seen photographs of only one and three individuals in the wild, respectively—are greatly imperiled by the industrialization of palm oil, which consumes its only home: the swampy lowlands of Peninsular Malaysia, Borneo, and Sumatra.
“These are extremely rare cats,” Sanderson said during a conversation in Suriname, where he was doing camera-trapping research to measure wild cat and prey densities. “The reason is the fishing cat and the flat-headed cat are both fish specialists and tied to water and the lowlands of Sumatra are being converted into oil palm plantations. So these small cats are in big trouble.”
Sanderson added that four of Borneo’s five cat species are vulnerable or endangered.
“Palm oil is the greatest threat to their survival,” he said.
Borneo’s “pygmy” elephants—pygmy because they are smaller than the elephants found in mainland Asia—are also suffering from growing demand for palm oil. The Sabah Wildlife Department, which manages parks in the state of Sabah in Malaysian Borneo, has reported an increase in the number of elephants maimed by snares set by plantation workers attempting to supplement their income by selling boar and deer meat to restaurants or eating it themselves. Elephants stumble into the traps and are snared. The resulting injury can lead to infection and even death. Young elephants are most at risk. Elephants, along with the critically endangered Sumatran rhino, are also losing habitat to plantations, which are often planted directly up to river banks, butting off key migration corridors.
  “Palm oil orphans” — as young orangutans displaced from their natural habitat have been termed by some environmentalists — at Nyaru Menteng Orangutan Rehabilitation and Reintroduction Center. Photos by Rhett A. Butler |
But it is orangutans—apes that share 97 percent of our DNA, use tools, arguably create art, and wean their young even longer than human mothers—that are the best-known victims of palm oil. The habitat of orangutans overlaps almost perfectly with the key palm oil-producing parts of Borneo and Sumatra. This circumstance has proven catastrophic for the “man of the forest.”
The effects of palm oil expansion on orangutans is particularly visible at Nyaru Menteng in Kalimantan, in the heart of Indonesian Borneo. While Nyaru Menteng is intended to be a rehabilitation center that enables orphaned orangutans to return to the wild, the facility is more like a sanctuary these days for the simple reason that suitable habitat in Borneo is being deforested so rapidly that it is becoming increasingly difficult to find locations for reintroduction.
Indeed, suitable habitat is becoming so scarce that scores of recently reintroduced orangutans have managed to win a taste of freedom only to be killed as their new homes are destroyed by loggers and oil palm developers. Economic returns from converting verdant rainforests into furniture, paper, and wood chips — and then using the land for oil palm plantations —have swiftly diminished the availability of sites for reintroduction, while dramatically boosting the number of orangutans in need of rescue.
So the orangutans must wait; more than 2,000 are currently in the rehabilitation system. But they are the lucky ones. For every orangutan housed in a center, half a dozen or more may have fallen victim to deforestation, been captured for the pet trade, or met their end at the blade of a machete or the blunt end of an iron bar. Estimates of orangutan deaths range from 1,500 to 5,000 per year, out of a population of only 54,000 in Borneo and 6,500 in Sumatra. (Borneo is divided between Indonesia and Malaysia; Sumatra is part of Indonesia.)
Meanwhile, their habitat continues to vanish as oil palm plantations metastasize across the Indonesian and Malaysian landscapes. In less than a generation, prime orangutan habitat in Kalimantan has declined by more than 50 percent, falling from 55,000 square miles in 1992 to fewer than 27,000 square miles today. Since 1975, the extent of primary forest cover in Sumatra has decreased by more than 90 percent.
Michelle Desilets, executive director of the Orangutan Land Trust, says she started to see the shift about five years ago. Relegated to ever smaller fragments of forest, wild orangutans began to face starvation as their food sources were depleted, forcing them to venture into newly established oil palm plantations where they feed on the young shoots of palms, destroying the tree before it produces any oil seeds.
Viewing the wild orangutans as pests, plantation managers started paying $10 to $20 for each dead orangutan — a strong incentive for a migrant worker who may earn just $10 per day.
 Nyaru Menteng |
“Our rescue teams began to be informed of wandering wild orangutans in human settlements,” Desilets told me, while cradling a baby orangutan in Nyaru Menteng. “We have found orangutans beaten to death with wooden planks and iron bars, butchered by machetes, beaten unconscious and buried alive, and doused with petrol and set alight. Since 2004, more and more orangutans in our centers have been rescued from areas within or near oil palm plantations, and over 90 percent of the infants up to three years of age come from these areas.”
Rising demand for palm oil—consumption by the United States jumped three-fold between 2005 and 2009 and continues to surge in rapidly developing countries like China and India—means that the situation is likely to continue. Unlike logged forest, which has the capacity to support at least some orangutans, oil palm plantations are not viable habitats for orangutans. If they can’t move to other areas — due to isolation or conflict with other orangutans — they will perish without human intervention.
The Center for Orangutan Protection, a grassroots group led by Hardi Baktiantoro, has taken intervention to a new level, mounting a guerrilla-style campaign against companies that are destroying orangutan habitat in Kalimantan. The group rigorously investigates new clearing, documenting environmental transgressions through video, photography, and GPS, which are mapped and presented via Google Earth. It then stages in-your-face demonstrations and issues media statements presenting evidence against plantation firms, government officials, and even NGOs.
The Center’s activities have not been welcomed by the palm oil industry. Facing threats, Hardi has had to hide his family and the group’s base of operations. The Center’s web site has been hacked and its communications tapped, while palm oil companies have offered Hardi tens of thousands of dollars in bribes in an effort to avoid the group’s scrutiny. But Hardi is defiant.
“My opinion is that as long as long as orangutan habitat is being destroyed we have to stop it,” he said during a meeting at a field site. “Anyone who destroys orangutan habitat and kills orangutans is my enemy.”
The plight of baby orangutans creates a vivid image, but it doesn’t tell the whole story. Although palm oil is a leading threat to orangutans, it is an important source of foreign exchange and employment in Indonesia and Malaysia. As the world’s highest yielding oilseed, the crop generates substantially more vegetable oil per acre than soy, canola (rapeseed), or corn, meaning that palm oil can help meet future demand for vegetable oil with less land, a point palm growers are quick to mention in any discussion over the environmental impacts of palm oil. Some even say the industry should be commended for its productivity. Some producers go even farther, arguing they should win carbon credits for avoiding deforestation that would otherwise have occurred if demand had been met by other less productive crops. Environmentalists scoff at the idea. But the conflict reflects the complexity around the crop.
A group of researchers, lead by Douglas Sheil of the Center for International Forestry Research (CIFOR), summed up current palm oil expansion as a series of trade offs.
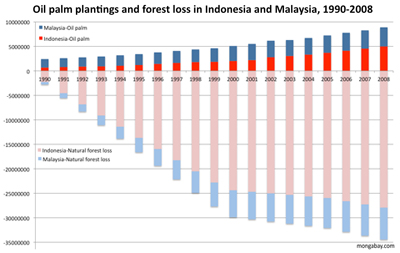 Expansion of the oil palm estate and natural forest loss in Indonesia and Malaysia, 1990-2008. Click image to enlarge |
“Implementing oil palm developments involves many tradeoffs,” Sheil and colleagues wrote in a report published in 2009. “Oil palm’s considerable profitability offers wealth and development where wealth and development are needed—but also threatens traditional livelihoods. It offers a route out of poverty, while also making people vulnerable to exploitation, misinformation and market instabilities. It threatens rich biological diversity—while also offering the finance needed to protect forest. It offers a renewable source of fuel, but also threatens to increase global carbon emissions.”
While palm oil generates substantial social benefits, including improved infrastructure, wealth and job creation, increased tax revenue for the state, there remain downsides, especially for forest-dependent people. Beyond the issues around establishing plantations, which often put developers in conflict with local people, labor concerns plague the industry. Working conditions are difficult and in many regions, the pay is low, even by local standards. Malaysian companies have difficulty finding domestic workers, so labor is usually imported—often illegally—from the Philippines and Indonesia. With uncertain legal status, and few alternatives once established on a plantation, foreign workers can be subject exploitation. An investigation by Indonesia’s Commission for Child Protection estimated in 2008 that some 72,000 children of Indonesian migrant workers were forced to work without regulated employment hours at plantations in the Malaysian state of Sabah alone. Arist Merdeka Sirait, the secretary general of the commission who announced the findings, said that children of plantations workers are not issued birth certificates, depriving them of the right to formal education.
In Papua, the Indonesian part of New Guinea, some local people believe oil palm expansion is part of a more sinister aim: subjection of indigenous Papuans to Indonesian rule. Many Papuans remain resistant to Indonesian control of the western half of New Guinea, which dates back to the 1963, but was never formally ratified in a free and fair process by the indigenous population. To quell dissent, the Indonesian government today maintains special restrictions in Papua and West Papua, the two provinces that presently make up Indonesian New Guinea. Under the rules, journalists are barring from reporting, freedom of expression is tightly controlled, political protests are quickly suppressed, books about democracy or democratic principles are banned from bookshops, and “special autonomy payments” are made to village heads. Some Papuans see the recent push by the Indonesian government to massively expand the oil palm estate in the provinces as a means to flood the region with Indonesians from other parts of the archipelago—people who have a stronger affinity toward Indonesia than the local population. The Environmental Investigative Agency’s report notes that to meet planned expansion of oil palm plantations in Indonesia New Guinea, Papua and West Papua will need to import a minimum of 200,000 workers, a substantial number is a place where the total population numbers less than 3 million and the proportion of native Papuans is declining. Palm oil could help make Papuans a minority in their own land.
“With the government planning at least five million hectares of plantations, a huge influx of migrant workers could take place, with the potential to greatly reduce the ethnic Papuan proportion of the population,” states the report. “Such a change will undoubtedly result in marginalization and alienation of indigenous Papuans in their own land.”
Given this mixed record, can a balance between palm oil production and social and environmental concerns be struck?
 Oil palm estate in Sumatra.  Rainforest in North Sulawesi. Photos by Rhett A. Butler. |
The industry believes so. In 2004 a group of stakeholders —including activists, investors, producers and retailers from around the world—formed the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) to develop a certification scheme for palm oil produced through environmentally and socially responsible ways. The criteria include: using natural pests and composting in place of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers whenever possible; implementing no-burn policies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and cut the risk of fires spreading into forest areas; sparing forests with high conservation value from development; taking measures to reduce air pollution; and creating catchment ponds to prevent palm oil mill effluent—a byproduct—from entering waterways where it would damage aquatic habitats. Social safeguards include restricting development from legitimately contested lands; adhering to the principle of “free prior informed consent” when engaging communities; maintaining basic health, labor, and safety standards for workers; and respecting the legal and customary rights of local people. The hope was that certified sustainable palm oil could be sold at a premium to recoup the increased costs that certification entails.
But while lauded as a potential path forward for the industry, the initiative stumbled out of the blocks. Unilever, the world’s largest corporate buyer of palm oil (1.3 million tons per year or 4 percent of the global market) and a strong supporter of RSPO, was soon targeted by Greenpeace in a colorful campaign, which included activists in orangutans suits invading Unilever shareholders meetings and offices. The campaign also included a detailed report accusing Indonesia-based PT Smart—one of the consumer product giant’s major suppliers and a company that claimed to be producing sustainable palm oil—of being engaged in damaging practices, notably the destruction of peatlands and rainforests. Fearing consumer backlash against its Dove soap products, Ben & Jerry’s ice cream, and other brands sold widely in Western markets, Unilever commissioned an investigation. The independent auditor reported PT Smart—which is owned by Indonesian conglomerate Sinar Mas—was actually worse than alleged. Unilever canceled its $32.6 million contract with the company, which would subsequently lose millions more in contracts, including deals with Kraft and Nestle.
“We are taking a stance against a supplier who is accused of breaking the law,” Unilever’s Chief Procurement Officer Marc Engel said at the time of the announcement. “We at Unilever are committed to sustainable sourcing.”
The incident sparked Unilever to more closely examine relationships with other companies. After a BBC documentary showed Duta Palma, another palm oil company, cutting down rainforest for new plantations, Unilever told its suppliers to stop sourcing from Duta Palma. Unilever feared that any link to suppliers with questionable practices could undermine its aim to have a fully traceable palm oil supply chain by 2015.
While Unilever has since launched an advertising campaign around its sourcing policies, its decision to get a better handle on its supply chain was a direct consequence of Greenpeace’s campaign. For Unilever, like other major consumer products companies, certified palm oil represents a way to mitigate risk rather than just appease activists. If consumers turn against Unilever products because they contain objectionable palm oil, the company may lose market share to competitors willing to adopt more transparent sourcing policies. Indeed some companies are already cutting back on, or completely eliminating, palm oil in their products. For example, Lush Cosmetics has not only replaced palm oil in its soaps but has launched a campaign against the crop. Cadbury New Zealand stopped using palm oil in its chocolates after consumer complaints—including a ban on Cadbury products by the Auckland Zoo over concerns of the impact of palm oil on orangutans. The World Bank, a key catalyst for oil palm development since the 1960s, even suspended lending to palm oil companies after it found environmental misconduct by Wilmar Plantations, one of its portfolio companies.
 Palm oil is now found in up to half of packaged processed foods in some markets. By virtue of its high yield, palm oil is a cheaper substitute than other vegetable oils. In an effort to reduce costs, some candymakers are using palm oil in place of cocoa butter in their milk chocolate products. Photo by Rhett A. Butler |
On the other hand, Nestle offers a case of what can go wrong when a company fails to respond to consumer concerns. In 2010, the food giant was caught in a firestorm when it attempted to censor a Greenpeace campaign that targeted its use of palm oil sourced from PT Smart, the same supplier accused in the Greenpeace report. There was blistering criticism—including 200,000 protest e-mails and the video of the gorilla finger, which went viral and was watched more than 1.3 million times after Nestle heavy-handedly tried to ban it. There were thousands of Twitter and Facebook messages on its corporate pages (including a Facebook page that asked whether a photo of an orangutan could get more fans than the Nestle page), and activists also brought to light a cadre of incidents Nestle would rather have forgotten, including its baby formula scandal of the 1970s and 1980s. At that point, Nestle canceled the PT Smart contract. But the damage had been done. Even though it was a small buyer of palm oil, a member of the RSPO, and its KitKat product contained only a microscopic amount of palm oil, the high profile campaign led Nestle to continue to be linked to rainforest destruction and orphaned orangutans well after it ended the relationship with the company. Other activists began to use the debacle to go after a bigger target, Cargill, the privately held American agricultural giant that is one of the largest deforesters on the planet. Although Nestle had stopped buying from PT Smart, it continued to source from Cargill, which Greenpeace, the Rainforest Action Network (RAN), and others had linked to forest clearing in Kalimantan, Indonesian Borneo.
RAN and other groups were hoping to pressure Cargill into severing ties with miscreants and adopting standards stronger than those endorsed by the RSPO, as other companies are now doing voluntarily. The pressure on Nestle eventually achieved just this: in May 2010 the food company removed all traces of palm oil from Sinar Mas from its products and launched new sourcing criteria to protect forests and respect the rights of local people. In short, Greenpeace—or as the group would say, the planet—had won. Cargill said it would investigate Sinar Mas and end its relationship with the company if it didn’t like what it found.
A few months later Sinar Mas issued a report it said cleared PT Smart of any wrongdoing. However, on closer examination of the results, it was apparent that Greenpeace’s accusations against the company were indeed accurate: PT Smart had broken Indonesian law and RSPO rules in eight out of the 11 concessions in Borneo and Sumatra that were independently audited. The ensuing scandal over Sinar Mas’s attempt to “spin” the auditor’s findings led Cargill to apply further pressure on the company, reiterating a demand that PT Smart stick to its commitment to certify all of its plantations by 2015. The incident was also a major black eye for the RSPO since PT Smart continued to hold up its membership in the organization as an example of its good environmental stewardship despite its well-publicized transgressions in Sumatra and Borneo.
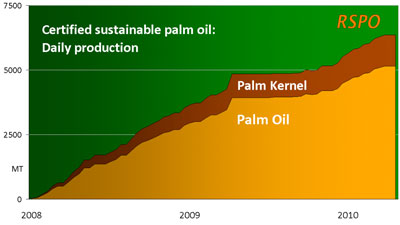
|
Despite the high-profile scandals, interest in RSPO is now growing, with demand for certified sustainable palm oil from European companies reaching nearly 100 percent of production in the first half of 2010. But, as illustrated by PT Smart and Cargill, the initiative still faces risks if more members are found to be violating its protocols. RSPO is still dogged by lack of oversight, lack punishment for cheaters, fundamental conflicts (for example, abiding by RSPO rules on sparing of high conservation value forest technically put Indonesian growers in violation of Indonesian law which requires concession holders to develop all land for plantations) and the perception, among critics, that its primary function is to legitimize continued expansion.
Ultimately the best incentive for credible RSPO is consumer demand. If consumers demonstrate with their wallets that they want credible eco-friendly palm oil, the palm oil industry will provide it. The cost of “greener” palm oil is not high—especially for buyers in rich countries. Research published by Lian Pin Koh, a scientist at ETH Zurich, and myself in January 2010 found that the average American consumer would only need to spend an extra 40 cents per year to cover the cost of switching his or her annual consumption of palm oil from conventional to certified sources. Europeans would, at most, need to cough up a euro or two. Consumers do have the power to change the industry.
Until consumers step up to support responsibly sourced palm oil, activists will continue to apply pressure on companies involved in questionable operations. One of the most poignant examples took place on Woodlark island—a tropical paradise off the coast of Papua New Guinea. The 200,000-acre island, which is home to a large number of endemic species, including the Woodlark Cuscus, a speckled nocturnal marsupial, supports 6,000 residents who live by gardening and hunting. But Woodlark’s natural bounty came under threat in 2007 when Vitroplant, a Malaysian plantation developer, signed a deal—without the consent of local people—to convert three-quarters of the island’s forests for oil palm. A small grassroots campaign against the project was massively amplified when Ecological Internet, an online activist group, got wind of the scheme. The Internet campaign triggered wider awareness among the press and policymakers in Britain, Australia, New Zealand, and Papua New Guinea. By January more than 3,000 protest e-mails had been sent to Sir Michael Somare, accusing the prime minister of leading Papua New Guinea from an “eco hero” to an “eco zero.” The country had won widespread acclaim from environmentalists following its performance at the December U.N. climate talks in Bali when delegate Kevin Conrad told the United States: “If you are not willing to lead [on climate change], then get out of the way.” The letter, sent by Ecological Internet, challenged Somare to do the same. The plans for the project were shelved shortly thereafter.
Dr. Simon Piyuwes, a physician who was one of the key leaders of the opposition against the project, had this to say when the government blocked the plantation.
“Woodlark Islanders live care-free lives in the midst of the ocean and their rich forest land. The forest and the animals play an irreplaceable importance in the lives of the islanders. It is a great relief to learn that the government has spared rare species that our earth desperately loves to keep. I, on behalf of the Woodlark Islanders, salute the government for the decision… I salute all organizations and individuals for signing up for this great issue. Our earth needs such cooperation.”
But palm oil isn’t the only energy product coming out of rainforests—jungles in the Amazon, Southeast Asia, and the Congo sit upon vast deposits of coal, oil and gas, and rare-earth metals. Extracting these resources, which are the building blocks and chief power source of the Internet age, is taking a heavy toll on forests and forest people—reminiscent of the fictional tale of Avatar. Some activists are now gearing up for an epic battle against corporate exploiters.
Related articles
Does chopping down rainforests for pulp and paper help alleviate poverty in Indonesia?

(01/13/2011) Over the past several years, Asia Pulp & Paper has engaged in a marketing campaign to represent its operations in Sumatra as socially and environmentally sustainable. APP and its agents maintain that industrial pulp and paper production — as practiced in Sumatra — does not result in deforestation, is carbon neutral, helps protect wildlife, and alleviates poverty. While a series of analyses and reports have shown most of these assertions to be false, the final claim has largely not been contested. But is conversion of lowland rainforests for pulp and paper really in Indonesia’s best economic interest?
Sales of RSPO-certified palm oil surge 225%
(01/10/2011) Sales of palm oil certified under the leading sustainability standard surged 225 percent in 2010, suggesting growing consumer interest in more responsibly-sourced palm oil.
Converting palm oil companies from forest destroyers into forest protectors

(01/02/2011) In efforts to save the world’s remaining rainforests great hopes have been pinned on “degraded lands” — deforested lands that are presently sitting idle in tropical countries. Optimists say shifting agriculture to such lands will help humanity produce enough food to meet growing demand without sacrificing forests and biodiversity and exacerbating social conflict. But to date, degraded lands remain an enigma, especially in Indonesia, where deforestation continues at a rapid pace. Degraded lands are often misclassified by various Indonesian ministries—land in a far-off province may be listed as “wasteland” by Jakarta, but in reality is blanked by verdant forest that sequesters carbon, houses wildlife, and affords communities with food, water, and other essentials. Granting logging and plantation concessions on these lands can result in conflict and environmental degradation.
Will Indonesia’s big REDD rainforest deal work?

(12/28/2010) Flying in a plane over the Indonesian half of the island of New Guinea, rainforest stretches like a sea of green, broken only by rugged mountain ranges and winding rivers. The broccoli-like canopy shows little sign of human influence. But as you near Jayapura, the provincial capital of Papua, the tree cover becomes patchier—a sign of logging—and red scars from mining appear before giving way to the monotonous dark green of oil palm plantations and finally grasslands and urban areas. The scene is not unique to Indonesian New Guinea; it has been repeated across the world’s largest archipelago for decades, partly a consequence of agricultural expansion by small farmers, but increasingly a product of extractive industries, especially the logging, plantation, and mining sectors. Papua, in fact, is Indonesia’s last frontier and therefore represents two diverging options for the country’s development path: continued deforestation and degradation of forests under a business-as-usual approach or a shift toward a fundamentally different and unproven model based on greater transparency and careful stewardship of its forest resources.
Lack of price premium for certified palm oil endangers sustainability initiative
(12/19/2010) The palm oil industry’s sustainability initiative is making considerable progress toward improving its environmental performance, but needs to do more to accelerate the adoption of responsible practices, argue researchers writing in mongabay.com’s open access journal Tropical Conservation Science.
RSPO to recognize secondary forests as conservation priority
(11/12/2010) The Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO), a body that sets environmental standards for palm oil production, has passed a resolution to reconfirm that secondary and degraded forests can classified as High Conservation Value (HCV) areas. The designation could increase the area of forest conserved within oil palm plantations provided it has high conservation significance, such as serving as habitat for endangered species like orangutans, Sumatran tigers, and rhinos.
U.S. companies should help drive push toward sustainable palm oil
(11/09/2010) U.S. companies should take a leadership role in helping ensure that palm oil production is sustainable and does not come at the cost of forests, climate, and communities, argues a new report published ahead of the annual meeting of the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO). The report, published by the National Wildlife Federation (NWF), says that while the U.S. is only a minor consumer of palm oil, its demand for the vegetable oil is fast rising, increasing four-fold since 2006. Palm oil, which is among the cheapest of vegetables owing to its high yield, is now found in up to 50 percent of packaged retail food products.
Dutch to use only certified palm oil by 2015
(11/04/2010) The Netherlands has committed to only using palm oil certified under the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) by 2015, providing a huge boost for the certification standard which aims to improve the social and environmental performance of the world’s most productive oil crop. The pledge makes the Netherlands the first country to commit itself to using only sustainable palm oil.
Scientists blast greenwashing by front groups

(10/27/2010) A group of prominent scientists has published an open letter challenging the objectivity of World Growth International, an NGO that claims to operate on behalf of the world’s poor, and its leader Alan Oxley, a former trade diplomat who also chairs ITS Global, a marketing firm. The letter, published online in several forums, slams World Growth and ITS Global as a front groups for forestry companies. The scientists note that while the groups have not disclosed their sources of funding, they assert ITS receives funding from Sinar Mas, an Indonesian conglomerate that controls Asia Pulp & Paper (APP), a forest products brand, and Sinar Mas Agro Resources & Technology, a palm oil firm, among other companies.
Misleading claims from a palm oil lobbyist
(10/23/2010) In an editorial published October 9th in the New Straits Times (“Why does World Bank hate palm oil?”), Alan Oxley, a former Australian diplomat who now serves as a lobbyist for logging and plantation companies, makes erroneous claims in his case against the World Bank and the International Finance Corp (IFC) for establishing stronger social and environmental criteria for lending to palm oil companies. It is important to put Mr. Oxley’s editorial in the context of his broader efforts to reduce protections for rural communities and the environment.
Corporations, conservation, and the green movement

(10/21/2010) The image of rainforests being torn down by giant bulldozers, felled by chainsaw-wielding loggers, and torched by large-scale developers has never been more poignant. Corporations have today replaced small-scale farmers as the prime drivers of deforestation, a shift that has critical implications for conservation. Until recently deforestation has been driven mostly by poverty—poor people in developing countries clearing forests or depleting other natural resources as they struggle to feed their families. Government policies in the ’60s, ’70s, and ’80s had a multiplier effect, subsidizing agricultural expansion through low-interest loans, infrastructure projects, and ambitious colonization schemes, especially in the Amazon and Indonesia. But over the past two decades, this has changed in many countries due to rural depopulation, a decline in state-sponsored development projects, the rise of globalized financial markets, and a worldwide commodity boom. Deforestation, overfishing, and other forms of environmental degradation are now primarily the result of corporations feeding demand from international consumers. While industrial actors exploit resources more efficiently and cause widespread environmental damage, they also are more sensitive to pressure from consumers and environmental groups. Thus in recent years, it has become easier—and more ethical—for green groups to go after corporations than after poor farmers.
The Nestlé example: how responsible companies could end deforestation

(10/06/2010) The NGO, The Forest Trust (TFT), made international headlines this year after food giant Nestlé chose them to monitor their sustainability efforts. Nestlé’s move followed a Greenpeace campaign that blew-up into a blistering free-for-all on social media sites. For months Nestle was dogged online not just for sourcing palm oil connected to deforestation in Southeast Asia—the focus of Greenpeace’s campaign—but for a litany of perceived social and environmental abuses and Nestlé’s reactions, which veered from draconian to clumsy to stonily silent. The announcement on May 17th that Nestlé was bending to demands to rid its products of deforestation quickly quelled the storm. Behind the scenes, Nestlé and TFT had been meeting for a number of weeks before the partnership was made official. But can TFT ensure consumers that Nestlé is truly moving forward on cutting deforestation from all of its products?
Compliance with national law not enough to meet int’l market demands
(10/05/2010) A UK-based cosmetics firm is severing ties with its palm oil supplier after a story in The Observer reported the Colombia-based company sought the eviction of peasant farmer families to develop a new oil palm plantation, reports the Guardian.
Eco-friendly palm oil initiative censures company linked to deforestation
(09/23/2010) The Roundtable On Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO), a body the sets standards for eco-friendly palm oil production, on Thursday said Indonesian palm oil producer Sinar Mas Agro Resources and Technology (SMART) breached its sustainability criteria and faces expulsion, reports AFP.
Another food goliath falls to palm oil campaign

(09/22/2010) One of the world’s biggest food makers, General Mills, has pledged to source only sustainable and responsible palm oil within five years time. With this announcement, General Mills becomes only the most recent food giant to pledge to move away from problematic sources of palm oil, which is used in everything from processed foods to health and beauty products. Nestle made a similar pledge earlier this year after a brutalizing social media campaign that lasted for months while Unilever, the world’s biggest palm oil buyer, has been working closely with green groups for years.
80% of tropical agricultural expansion between 1980-2000 came at expense of forests
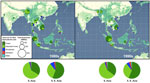
(09/02/2010) More than 80 percent of agricultural expansion in the tropics between 1980 and 2000 came at the expense of forests, reports research published last week in the early online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). The study, based on analysis satellite images collected by the United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) and led by Holly Gibbs of Stanford University, found that 55 percent of new agricultural land came at the expense of intact forests, while 28 percent came from disturbed forests. Another six percent came from shrub lands.

(08/19/2010) Sinar Mas, an Indonesian conglomerate whose holdings include Asia Pulp and Paper, a paper products brand, and PT Smart, a palm oil producer, was sharply rebuked Wednesday over a recent report where it claimed not to have engaged in destruction of forests and peatlands. At least one of its companies, Golden Agri Resources, may now face an investigation for deliberately misleading shareholders in its corporate filings.

(07/29/2010) Many of the environmental issues facing Indonesia are embodied in the plight of the orangutan, the red ape that inhabits the islands of Borneo and Sumatra. Orangutan populations have plummeted over the past century, a result of hunting, habitat loss, the pet trade, and human-ape conflict. Accordingly, governments, charities, and concerned individuals have ploughed tens of millions of dollars into orangutan conservation, but have little to show in terms of slowing or reversing the decline. The same can be said about forest conservation in Indonesia: while massive amounts of money have been put toward protecting and sustainable using forests, the sum is dwarfed by the returns from converting forests into timber, rice, paper, and palm oil. So orangutans—and forests—continue to lose out to economic development, at least as conventionally pursued. Poor governance means that even when well-intentioned measures are in place, they are often undermined by corruption, apathy, or poorly-designed policies. So is there a future for Indonesia’s red apes and their forest home? Erik Meijaard, an ecologist who has worked in Indonesia since 1993 and is considered a world authority on orangutan populations, is cautiously optimistic, although he sees no ‘silver bullet’ solutions.
How Greenpeace changes big business

(07/22/2010) Tropical deforestation claimed roughly 13 million hectares of forest per year during the first half of this decade, about the same rate of loss as the 1990s. But while the overall numbers have remained relatively constant, they mask a transition of great significance: a shift from poverty-driven to industry-driven deforestation and geographic consolidation of where deforestation occurs. These changes have important implications for efforts to protect the world’s remaining tropical forests in that environmental groups now have identifiable targets that may be more responsive to pressure on environmental concerns than tens of millions of impoverished rural farmers. In other words, activists have more leverage than ever to impact corporate behavior as it relates to deforestation. A prime example of this power is evident in a string of successful Greenpeace campaigns, which have targeted some of the largest drivers of deforestation, including the palm oil industry in Indonesia and Malaysia and the soy and cattle industries in the Brazilian Amazon. The campaigns have shared a common approach: target large, conspicuous consumer-facing companies that sell in western markets.
Indonesia’s plan to save its rainforests

(06/14/2010) Late last year Indonesia made global headlines with a bold pledge to reduce deforestation, which claimed nearly 28 million hectares (108,000 square miles) of forest between 1990 and 2005 and is the source of about 80 percent of the country’s greenhouse gas emissions. President Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono said Indonesia would voluntarily cut emissions 26 percent — and up to 41 percent with sufficient international support — from a projected baseline by 2020. Last month, Indonesia began to finally detail its plan, which includes a two-year moratorium on new forestry concession on rainforest lands and peat swamps and will be supported over the next five years by a one billion dollar contribution by Norway, under the Scandinavian nation’s International Climate and Forests Initiative. In an interview with mongabay.com, Agus Purnomo and Yani Saloh of Indonesia’s National Climate Change Council to the President discussed the new forest program and Norway’s billion dollar commitment.
Nestle caves to activist pressure on palm oil

(05/17/2010) After a two month campaign against Nestle for its use of palm oil linked to rainforest destruction spearheaded by Greenpeace, the food giant has given in to activists’ demands. The Swiss-based company announced today in Malaysia that it will partner with the Forest Trust, an international non-profit organization, to rid its supply chain of any sources involved in the destruction of rainforests. “Nestle’s actions will focus on the systematic identification and exclusion of companies owning or managing high risk plantations or farms linked to deforestation,” a press release from the company reads, adding that “Nestle wants to ensure that its products have no deforestation footprint.”
Brazil launches major push for sustainable palm oil in the Amazon
(05/07/2010) Brazilian President Lula da Silva on Thursday laid out plans to expand palm oil production in the Amazon while minimizing risk to Earth’s largest rainforest. The plan, called the Program for Sustainable Production of Palm Oil (O Programa de Produção Sustentável de Óleo de Palma), will provide $60 million to promote cultivation of oil palm in abandoned and degraded agricultural areas, including long-ago deforested lands used for sugar cane and pasture. Brazilian officials claim up to 50 million hectares of such land exist in the country.
Nestle’s palm oil debacle highlights current limitations of certification scheme
(03/26/2010) Last week Nestle, the world’s largest food processor, was caught in a firestorm when it attempted to censor a Greenpeace campaign that targeted its use of palm oil sourced from a supplier accused of environmentally-damaging practices. The incident brought the increasingly raucous debate over palm oil into the spotlight and renewed questions over an industry-backed certification scheme that aims to improve the crop’s environmental performance.
Commodity trade and urbanization, rather than rural poverty, drive deforestation

(02/07/2010) Deforestation is increasingly correlated to urban population growth and trade rather than rural poverty, suggesting that measures proposed to reduce deforestation will be ineffective if they fail to address demand for commodities produced on forest lands, argues a new paper published in Nature GeoScience.
Orangutans vs palm oil in Malaysia: setting the record straight

(01/16/2010) The Malaysian palm oil industry has been broadly accused of contributing to the dramatic decline in orangutan populations in Sabah, a state in northern Borneo, over the past 30 years. The industry has staunchly denied these charges and responded with marketing campaigns claiming the opposite: that oil palm plantations can support and nourish the great red apes. The issue came to a head last October at the Orangutan Colloquium held in Kota Kinabalu. There, confronted by orangutan biologists, the palm oil industry pledged to support restoring forest corridors along rivers in order to help facilitate movement of orangutans between remaining forest reserves across seas of oil palm plantations. Attending NGOs agreed that they would need to work with industry to find a balance that would allow the ongoing survival of orangutans in the wild. Nevertheless the conference was still marked by much of the same rhetoric that has characterized most of these meetings — chief palm oil industry officials again made dubious claims about the environmental stewardship of the industry. However this time there was at least acknowledgment that palm oil needs to play an active role in conservation.
Consumers should help pay the bill for ‘greener’ palm oil

(01/12/2010) Palm oil is one of the world’s most traded and versatile agricultural commodities. It can be used as edible vegetable oil, industrial lubricant, raw material in cosmetic and skincare products and feedstock for biofuel production. Growing global demand for palm oil and the ensuing cropland expansion has been blamed for a wide range of environmental ills, including tropical deforestation, peatland degradation, biodiversity loss and CO2 emissions. In response to these concerns, a group of stakeholders—including activists, investors, producers and retailers—formed the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) to develop a certification scheme for palm oil produced through environmentally- and socially-responsible ways. It is widely anticipated that the creation of a premium market for RSPO-certified sustainable palm oil (CSPO) would incentivize palm oil producers to improve their management practices.
Blackwashing by NGOs, greenwashing by corporations, threatens environmental progress
(11/12/2009) Misinformation campaigns by both corporations and environmental groups threaten to undermine efforts to conserve biodiversity and reduce environmental degradation, argues a new paper published in the journal Biotropica. Growing concerns over climate change and unsustainable resource extraction have put companies that exploit the environment in the spotlight. Some firms have responded by taking measures to reduce their environmental impact. Others have alternatively engaged in sophisticated marketing campaigns intended to mislead consumers on their environmental performance, maintaining that environmentally-destructive practices are instead benign. At the same time some activist groups have been guilty of exaggerating claims of environmental misconduct in order to boost support for their campaigns and therefore their fundraising efforts.
Palm oil developers push into Indonesia’s last frontier: Papua
(11/10/2009) Oil palm developers in the Indonesian half of New Guinea are signing questionable deals that exploit local communities and put important forest ecosystems at risk, alleges a new report from Environmental Investigation Agency (EIA) and Telapak.
Palm oil both a leading threat to orangutans and a key source of jobs in Sumatra

(09/24/2009) Of the world’s two species of orangutan, a great ape that shares 96 percent of man’s genetic makeup, the Sumatran orangutan is considerably more endangered than its cousin in Borneo. Today there are believed to be fewer than 7,000 Sumatran orangutans in the wild, a consequence of the wildlife trade, hunting, and accelerating destruction of their native forest habitat by loggers, small-scale farmers, and agribusiness. Gunung Leuser National Park in North Sumatra is one of the last strongholds for the species, serving as a refuge among paper pulp concessions and rubber and oil palm plantations. While orangutans are relatively well protected in areas around tourist centers, they are affected by poorly regulated interactions with tourists, which have increased the risk of disease and resulted in high mortality rates among infants near tourist centers like Bukit Lawang. Further, orangutans that range outside the park or live in remote areas or on its margins face conflicts with developers, including loggers, who may or may not know about the existence of the park, and plantation workers, who may kill any orangutans they encounter in the fields. Working to improve the fate of orangutans that find their way into plantations and unprotected community areas is the Orangutan Information Center (OIC), a local NGO that collaborates with the Sumatran Orangutan Society (SOS).
Britain bans palm oil ad campaign
(09/09/2009) Britain’s Advertising Standards Authority (ASA), a group that regulates advertisements, has again banned “misleading” ads by the palm oil industry, reports the Guardian. ASA ruled that a campaign run by the Malaysian Palm Oil Council (MPOC) makes dubious claims, including that palm oil is the “only product able to sustainably and efficiently meet a larger portion of the world’s increasing demand for oil crop-based consumer goods, foodstuffs and biofuels.” The ad said criticism over “rampant deforestation and unsound environmental practices” were part of “protectionist agendas” not based on scientific fact. ASA held the ad breached several of its advertising standards codes, including “substantiation,” “truthfulness,” and “environmental claims.” In rebuking the MPOC, the ASA said that the merits of new eco-certification scheme promoted by the palm oil industry is “still the subject of debate” and that the ad’s attacks on detractors implied that all criticisms of the palm oil industry “were without a valid or scientific basis.”
Rehabilitation not enough to solve orangutan crisis in Indonesia

(08/20/2009) A baby orangutan ambles across the grass at the Borneo Orangutan Survival Foundation’s Nyaru Menteng rehabilitation center in Central Kalimantan, in the heart of Indonesian Borneo. The ape pauses, picks up a stick and makes his way over to a plastic log, lined with small holes. Breaking the stick in two, he pokes one end into a hole in an effort to extract honey that has been deposited by a conservation worker. His expression shows the tool’s use has been fruitful. But he is not alone. To his right another orangutan has turned half a coconut shell into a helmet, two others wrestle on the lawn, and another youngster scales a papaya tree. There are dozens of orangutans, all of which are about the same age. Just outside the compound, dozens of younger orangutans are getting climbing lessons from the Borneo Orangutan Survival Foundation (BOS) staff, while still younger orangutans are being fed milk from bottles in a nearby nursery. Still more orangutans—teenagers and adults—can be found on “Orangutan Island” beyond the center’s main grounds. Meanwhile several recently wild orangutans sit in cages. This is a waiting game. BOS hopes to eventually release all of these orangutans back into their natural habitat—the majestic rainforests and swampy peatlands of Central Kalimantan, on the island of Borneo. But for many, this is a fate that may never be realized.
Cadbury dumps palm oil after consumer protests

(08/17/2009) Cadbury New Zealand, responding to widespread consumer protests, will stop adding palm oil to its milk chocolate products, reports the New Zealand Herald. The candy-maker substituted palm oil and other vegetable fat for cocoa butter earlier this year. The company cited cost savings for the decision, but the move triggered outcry from environmental groups who blame palm oil production for destruction of rainforests across Indonesia and Malaysia, key habitat for orangutans and other endangered species. Concerns that Cadbury chocolate could be imperiling orangutans led the Auckland Zoo and others to ban Cadbury products. Meanwhile consumers swamped the company with letters and petitions protesting its use of palm oil.
Issues around palm oil development prove complex, controversial
(08/12/2009) A new report from published by the Center for International Forestry Research (CIFOR) highlights the benefits — and controversies — of large-scale expansion of oil palm agriculture in Southeast Asia. The review, titled “The impacts and opportunities of oil palm in Southeast Asia: What do we know and what do we need to know?”, notes that while oil palm is a highly productive and profitable crop, there are serious concerns about its environmental and social impact when established on disputed land or in place of tropical forests and peatlands.
LUSH cosmetics launches campaign against palm oil
(08/10/2009) LUSH Cosmetics, a leading cosmetics-maker, will no longer use palm oil due to environmental concerns over its production. LUSH, which is now selling a palm oil-free soap, has launched a two-pronged campaign to make consumers aware of the impacts of palm cultivation on tropical forests and encourage other consumer-products companies, including Procter & Gamble, Unilever and Nestle, to reformulate their products using alternatives to palm oil.
Limit palm oil development to lands that store less than 40 tons of carbon/ha – study
(08/06/2009) A new study finds oil palm plantations store less carbon than previously believed, suggesting that palm oil produced through the conversion of tropical forests carries a substantial carbon debt.

