Forest conservation via REDD may be ineffective without addressing commodity consumption and trade, argues a new paper that looks at the implications of changing drivers of deforestation on new policy measures to protect forests.
Deforestation is increasingly correlated to urban population growth and trade rather than rural poverty, suggesting that measures proposed to reduce deforestation will be ineffective if they fail to address demand for commodities produced on forest lands, argues a new paper published in Nature GeoScience.
Using newly available, spatially explicit analysis of tropical forest loss, Ruth S. DeFries, Thomas Rudel, Maria Uriarte and Matthew Hansen determined that from 2000-2005, rural population growth was not associated with forest loss, “indicating the importance of urban-based and international demands for agricultural products as drivers of deforestation.” The results are a departure from research for earlier periods that has shown rural population growth to be the primary driver of deforestation.

|
“Landscapes with stabilizing or depopulating populations are likely to exacerbate rather than reduce pressure to clear forests, primarily because urbanization raises consumption levels and increases demand for agricultural products. Urban consumers generally eat more processed foods and animal products than rural consumers, thereby inducing commercial production of crops and livestock,” write the authors. “This pattern contradicts the argument that pressures on forests will decline as local populations urbanize.”
Industrial agriculture has become a booming business in the tropics over the past two decades. Driven by international demand for commodities, vast areas of rainforest have been razed, burned, and converted for extensive soy farms, sugar cane fields, cattle ranches, and oil palm, rubber, and timber plantations. So while many countries are experiencing rural depopulation, which reduces the pool of subsistence farmers that traditionally clear forests for small-scale agriculture, deforestation rates have remained roughly constant over the period.
Accordingly, the authors argue that measures like the proposed REDD (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and forest Degradation) mechanism will need to go beyond sustainable development schemes for subsistence cultivators and the establishment of protected areas in rural landscapes to be effective in slowing forest loss.
“We therefore suggest that policies to reduce deforestation among local, rural populations will not address the main cause of deforestation in the future. Rather, efforts need to focus on reducing deforestation for industrial-scale, export-oriented agricultural production, concomitant with efforts to increase yields in non-forested lands to satisfy demands for agricultural products.”
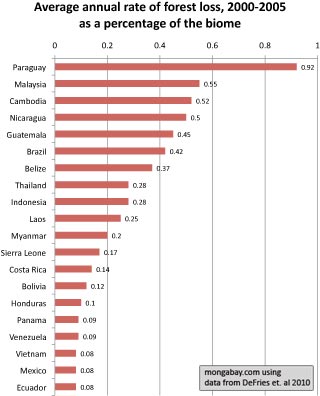 Average annual rate of forest loss, 2000-2005 as a percentage of the original extent of the biome (rather than the extent of forest in 2000). Click image to enlarge. |
But the results have implications beyond REDD. The study undermines claims by industry groups — including loggers and oil palm plantation developers — that efforts to fight deforestation will exacerbate rural poverty. Indeed, other research suggests that large landowners and corporations are the biggest beneficiaries of large-scale forest conversion. For example, a study published last year in Science found that Amazon deforestation fails to sustain long-term economic growth for rural populations. Amazon communities are not richer, better educated, or healthier after forest clearing — most of the benefits of conversion accrue to developers.
The new paper also lends credibility to the argument that the shift in the underlying drivers of deforestation may offer new opportunities to protect forests in that it is easier, and more ethical, for environmental lobby groups to target corporations and enterprises rather than tens of millions of poor farmers who are simply trying to put food on the table for their families.
Ruth S. DeFries, Thomas Rudel, Maria Uriarte and Matthew Hansen. Deforestation driven by urban population growth and agricultural trade in the twenty-first century. Nature Geoscience. published online: 7 February 2010 | DOI: 10.1038/NGEO756
Related articles
Changing drivers of deforestation provide new opportunities for conservation

(12/09/2009) Tropical deforestation claimed roughly 13 million hectares of forest per year during the first half of this decade, about the same rate of loss as the 1990s. But while the overall numbers have remained relatively constant, they mask a transition of great significance: a shift from poverty-driven to industry-driven deforestation and geographic consolidation of where deforestation occurs. These changes have important implications for efforts to protect the world’s remaining tropical forests in that environmental lobby groups now have identifiable targets that may be more responsive to pressure on environmental concerns than tens of millions of impoverished rural farmers. In other words, activists have more leverage than ever to impact corporate behavior as it relates to deforestation.
In absence of measures to address consumption, REDD may fail to protect forests

(12/02/2009) Rising demand for timber and agricultural products could work against a proposed initiative to reduce emissions from deforestation and degradation (REDD), warns a new report from the Environmental Investigation Agency (EIA). The briefing, Putting the Brakes on Drivers of Forest Destruction: A Shared Responsibility, says that investment in REDD will not be enough to protect forests if the underlying drivers of deforestation — namely consumption — are not addressed. It urges negotiators to re-insert critical text that has been dropped from the working text on REDD ahead of next week’s climate change conferences in Copenhagen.
In absence of measures to address consumption, REDD may fail to protect forests

(12/02/2009) Rising demand for timber and agricultural products could work against a proposed initiative to reduce emissions from deforestation and degradation (REDD), warns a new report from the Environmental Investigation Agency (EIA). The briefing, Putting the Brakes on Drivers of Forest Destruction: A Shared Responsibility, says that investment in REDD will not be enough to protect forests if the underlying drivers of deforestation — namely consumption — are not addressed. It urges negotiators to re-insert critical text that has been dropped from the working text on REDD ahead of next week’s climate change conferences in Copenhagen.
Shift from poverty-driven to industry-driven deforestation may help conservation
(08/06/2008) A shift from poverty-driven deforestation to industry-driven deforestation in the tropics may offer new opportunities for forest conservation, argues a new paper published in the journal Trends in Ecology & Evolution. Citing research showing a transition in the forces driving tropical forest destruction, Rhett A, Butler of mongabay.com, a tropical forest web site, and William F. Laurance of the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute in Panama suggest that the “industrialization” of deforestation provides environmental lobby groups with identifiable targets that may be more responsive to pressure on environmental concerns than tens of millions of impoverished rural farmers.

