Fires in Central America worsen air quality in Texas
Fires in Central America worsen air quality in Texas
mongabay.com
October 10, 2006
Agricultural fires in Central America can impact air quality and climate in Texas, Oklahoma, and other parts of the southern United States according to new research from NASA.
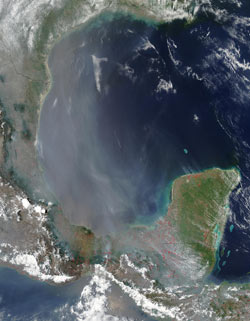 A thick haze of smoke covers much of the Gulf of Mexico and southern Texas in this true-color Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) image from the Aqua satellite on May 9, 2003. Smoke from fires (red dots) burning across southern Mexico and Central America spread northward. Click image to enlarge. Credit: NASA/MODIS Rapid Response Team Credit: NASA/MODIS Rapid Response Team
|
The study, published in the July 26, 2006 Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, found that in the spring of 2003 pollution from fires in the Yucatan Peninsula and southern Mexico reached parts of the United States. The smoke “degraded visibility and air quality in coastal regions along the Gulf of Mexico and resulted in the greatest concentration of small particulate matter in southern Texas since 1998,” according to a release from NASA.
“By blocking incoming sunlight, the smoke plumes also cooled surface air temperatures over land. But higher in the atmosphere the smoke absorbed solar radiation and warmed temperatures. This created a circulation pattern that trapped smoke aerosols in the lower atmosphere, worsening air quality,” explained NASA.
The space agency said that the research may help scientists improve weather forecasts by better understanding the role of smoke and aerosols on climate.
Fires are set on a seasonal basis in Central America for land-clearing and agricultural waste (biomass) burning.
The paper follows up on research published last year indicating that tropical deforestation can affect US climate. Using data from the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies, Duke University researchers found that deforestation in the Amazon region of South America influences rainfall in Texas and in the Gulf of Mexico, while forest loss in Central Africa affects precipitation patterns in the upper and lower Midwest of the United States.
NASA: Central American Fires Impact U.S. Air Quality and Climate
This article uses quotes and information from a NASA news release.
>