Wales outlines Renewable Energy Route Map: bioenergy, marine, wind power can meet all electricity needs by 2025
An important step on the path to making Wales a low carbon energy economy was taken today when the Minister for Environment, Sustainability and Housing, Jane Davidson launched the Renewable Energy Route Map. The route map sets out an ambitious programme aimed at transforming the way Wales produces and uses energy as part of the Welsh Assembly Government’s commitment to tackling climate change.
Policy makers believe that with Wales’ coastline, geography and climate, it is quite feasible for the nation within 20 years to produce more electricity from renewables than it consumes as a nation.
With sufficient innovation and investment, the right Government framework and public support, Wales could produce some 33TWhr per year of electricity (its current consumption is around 24 TWhr) from renewable sources. The potential for 2025 looks as follows:
The map sets out specific actions on how Wales can meet the renewable electricity self-sufficiency objective, how biomass resources could be used for significant renewable heat production, and how the nation can support challenging energy efficiency and small-scale micro-generation ambitions.
Renewable resources
Marine
Wales' marine energy resources can be split into 3 components: wave-power, tidal stream and tidal range. The tidal range is better known as barrage and lagoon projects. The Assembly Government has started down this path with financial support for early stage wave and tidal stream projects.
Possible actions include:
Wind
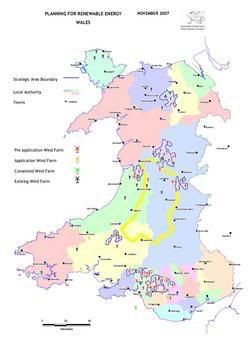 Wales has shown the way with its TAN8 renewables planning guidance, for large on shore wind farms. Offshore, Wales already has the North Hoyle wind-farm off Prestatyn and other major projects are at various stages of development (map shows current wind projects).
Wales has shown the way with its TAN8 renewables planning guidance, for large on shore wind farms. Offshore, Wales already has the North Hoyle wind-farm off Prestatyn and other major projects are at various stages of development (map shows current wind projects).
Possible actions under the Renewable Energy Route Map include:
Biomass and energy from waste
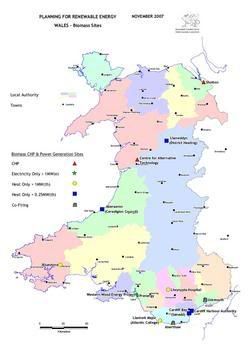 Biomass-energy involves the use the forestry products and energy crops from land and in some cases wastes either directly converted into energy (dedicated biomass power plants, co-firing), or through bio-refining into other materials to produce electricity, heat or transport fuels-either separately or in combination (map shows current biomass projects in Wales).
Biomass-energy involves the use the forestry products and energy crops from land and in some cases wastes either directly converted into energy (dedicated biomass power plants, co-firing), or through bio-refining into other materials to produce electricity, heat or transport fuels-either separately or in combination (map shows current biomass projects in Wales).
Possible actions include:
 energy :: sustainability :: biofuels :: biomass :: bioenergy :: wind power :: marine power :: renewables :: Wales ::
energy :: sustainability :: biofuels :: biomass :: bioenergy :: wind power :: marine power :: renewables :: Wales ::
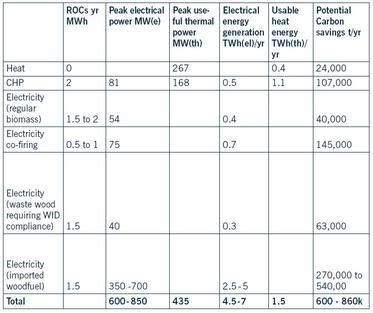
An interim analysis indicates that biomass (both indigenous and imported) might annually generate some 4 to 7TWhr pa of electricity and about 1.5TWh pa of heat (table, click to enlarge) and that a policy which gives highest priority ‘ to local biomass for local energy production’ is likely to meet most sustainable development objectives. This might be achieved by 2015, especially if public sector projects can be used as exemplars as soon as possible.
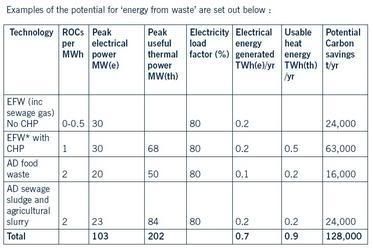
Examples of the potential for ‘energy from waste’ are set out in the table above (click to enlarge).
Energy efficiency, micro-generation and distributed generation
Energy Efficiency
Wales wants to ensure that all new buildings are built to the highest possible low carbon standards. Higher standards through devolved Building Regulations would be aimed at delivering the aspiration for all new buildings to be zero carbon by 2011.
The Assembly Government also commits to expanding services available through the new Sustainable Energy Network as well as encouraging rapid progress with smart meter installations and take up of support from energy suppliers under the new carbon emissions reduction target, CERT initiative.
Micro-generation
Possible actions include:
-issue planning guidance to make micro generation easier to install – in particular for:
-biomass electricity or heat generating units, especially for larger properties or community projects
-increasingly build micro-generation into our locally funded programmes, as part of the commitment to zero carbon buildings
-under its green jobs strategy, building on Wales’ already substantial solar photovoltaic industry to be an effective champion for this highly promising technology
-increase the role of renewable/alternative energy solutions under the Home Energy Efficiency Service.
Distributed generation
Possible actions include:
References:
Welsh Assembly Government: Route to low carbon future for Wales mapped out by Jane Davidson - February 19, 2008.
Welsh Assembly Government: Renewable Energy Route Map for Wales: consultation on way forward to a leaner, greener and cleaner Wales [*.pdf], February 2008.
Welsh Assembly Government: A Guide to the New Renewable Energy Route Map for Wales
Consultation on the way forward to a leaner, greener and cleaner Wales [*.pdf], February 2008.
Policy makers believe that with Wales’ coastline, geography and climate, it is quite feasible for the nation within 20 years to produce more electricity from renewables than it consumes as a nation.
With sufficient innovation and investment, the right Government framework and public support, Wales could produce some 33TWhr per year of electricity (its current consumption is around 24 TWhr) from renewable sources. The potential for 2025 looks as follows:
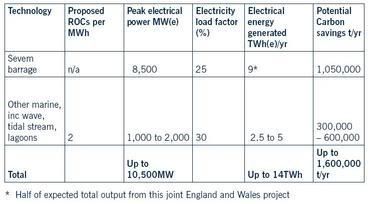
- marine power (wave, tidal stream, tidal range): up to 14TWh of electricity
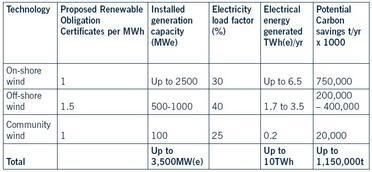
- wind (both on and offshore): up to 10 TWh of electricity
- bioenergy from biomass and waste: 7.7 TWh of electricity and 2.4 TWh of heat
The map sets out specific actions on how Wales can meet the renewable electricity self-sufficiency objective, how biomass resources could be used for significant renewable heat production, and how the nation can support challenging energy efficiency and small-scale micro-generation ambitions.
Renewable resources
Marine
Wales' marine energy resources can be split into 3 components: wave-power, tidal stream and tidal range. The tidal range is better known as barrage and lagoon projects. The Assembly Government has started down this path with financial support for early stage wave and tidal stream projects.
Possible actions include:
- support opportunities for and encourage marine feasibility studies and research
- examine whether EU Convergence Funds could be used to run a competition to identify the best tidal lagoon site in Wales and support the preparatory phases of constructing perhaps the world’s first tidal-energy lagoon
- develop a Wales marine energy action plan to take forward all the marine proposals
Wind
 Wales has shown the way with its TAN8 renewables planning guidance, for large on shore wind farms. Offshore, Wales already has the North Hoyle wind-farm off Prestatyn and other major projects are at various stages of development (map shows current wind projects).
Wales has shown the way with its TAN8 renewables planning guidance, for large on shore wind farms. Offshore, Wales already has the North Hoyle wind-farm off Prestatyn and other major projects are at various stages of development (map shows current wind projects).Possible actions under the Renewable Energy Route Map include:
- continue to pursue the proposals in Tan 8 and monitor the uptake of wind farm sites before a further review starts in the light of this and other consultations
- develop with partners a strategic bid for a Convergence Fund project aimed at delivering a series of community scale wind energy generation projects across the eligible area
- support UK work on a strategic environmental assessment (SEA) for offshore wind generation in English and Welsh territorial waters.
Biomass and energy from waste
 Biomass-energy involves the use the forestry products and energy crops from land and in some cases wastes either directly converted into energy (dedicated biomass power plants, co-firing), or through bio-refining into other materials to produce electricity, heat or transport fuels-either separately or in combination (map shows current biomass projects in Wales).
Biomass-energy involves the use the forestry products and energy crops from land and in some cases wastes either directly converted into energy (dedicated biomass power plants, co-firing), or through bio-refining into other materials to produce electricity, heat or transport fuels-either separately or in combination (map shows current biomass projects in Wales).Possible actions include:
- support the development of community heat and power units under a new wood energy business scheme- which could be funded through EU Structural Fund programmes;
- ask designers and contractors to use biomass-energy plants where possible in the development of residential and commercial properties on Assembly Government owned land;
- provide advice through the newly formed Sustainable Energy Network on opportunities for community heat and power schemes across Wales;
- encourage all other public sector bodies to support biomass energy developments, where possible through long term feedstock purchase contracts which give growers the confidence to make the necessary investments;
- consider the scope for requiring biomass combined heat and power for larger-scale developments
- support larger scale biomass projects where the fuel source is demonstrably sustainable
- support the development of community heat and power units under a new wood energy business scheme which could be funded through EU Structural Fund programmes
- publish for consultation a biomass energy strategy/action plan which fully explores these complexities for Wales
- explore how the new Better Woodlands for Wales grant scheme could be more closely targeted or arrangements made to encourage cooperative action on the part of groups of farmers to identify and source biomass material for specific initiatives
- examine skills needs with the Sector Skills Councils, to ensure an effective micro-generation equipment supply and fitting sector.
- produce a ‘best-practice’ design guide for new waste management facilities with exemplar facilities illustrating to developers and local authorities what can be achieved
 energy :: sustainability :: biofuels :: biomass :: bioenergy :: wind power :: marine power :: renewables :: Wales ::
energy :: sustainability :: biofuels :: biomass :: bioenergy :: wind power :: marine power :: renewables :: Wales :: An interim analysis indicates that biomass (both indigenous and imported) might annually generate some 4 to 7TWhr pa of electricity and about 1.5TWh pa of heat (table, click to enlarge) and that a policy which gives highest priority ‘ to local biomass for local energy production’ is likely to meet most sustainable development objectives. This might be achieved by 2015, especially if public sector projects can be used as exemplars as soon as possible.
Examples of the potential for ‘energy from waste’ are set out in the table above (click to enlarge).
Energy efficiency, micro-generation and distributed generation
Energy Efficiency
Wales wants to ensure that all new buildings are built to the highest possible low carbon standards. Higher standards through devolved Building Regulations would be aimed at delivering the aspiration for all new buildings to be zero carbon by 2011.
The Assembly Government also commits to expanding services available through the new Sustainable Energy Network as well as encouraging rapid progress with smart meter installations and take up of support from energy suppliers under the new carbon emissions reduction target, CERT initiative.
Micro-generation
Possible actions include:
-issue planning guidance to make micro generation easier to install – in particular for:
- Roof mounted solar heat and solar (photo-voltaic) electric panels
- Ground, water and air source powered heat pumps
- Building mounted micro-wind electricity turbines or stand alone small wind turbines
-biomass electricity or heat generating units, especially for larger properties or community projects
-increasingly build micro-generation into our locally funded programmes, as part of the commitment to zero carbon buildings
-under its green jobs strategy, building on Wales’ already substantial solar photovoltaic industry to be an effective champion for this highly promising technology
-increase the role of renewable/alternative energy solutions under the Home Energy Efficiency Service.
Distributed generation
Possible actions include:
- support community-sized wind, biomass and hydroelectric schemes through the provision of grants through the climate change framework of the EU Convergence Funds programme
- guide businesses interested in generating their own renewable energy
- explore the scope for a CHP scheme for the Cathays Park area of Cardiff where the main Assembly Government office is located
- explore the scope for developing energy supply companies (ESCo) in Wales that could support off-grid developments and innovative energy efficiency packages.
References:
Welsh Assembly Government: Route to low carbon future for Wales mapped out by Jane Davidson - February 19, 2008.
Welsh Assembly Government: Renewable Energy Route Map for Wales: consultation on way forward to a leaner, greener and cleaner Wales [*.pdf], February 2008.
Welsh Assembly Government: A Guide to the New Renewable Energy Route Map for Wales
Consultation on the way forward to a leaner, greener and cleaner Wales [*.pdf], February 2008.
 --------------
--------------
 The 16th European Biomass Conference & Exhibition - From Research to Industry and Markets - will be held from 2nd to 6th June 2008, at the Convention and Exhibition Centre of FeriaValencia, Spain. Early bird fee registration ends 18th April 2008.
The 16th European Biomass Conference & Exhibition - From Research to Industry and Markets - will be held from 2nd to 6th June 2008, at the Convention and Exhibition Centre of FeriaValencia, Spain. Early bird fee registration ends 18th April 2008.









0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Links to this post:
Create a Link
<< Home