- Scientists discovered more than 1,000 previously unknown species during a decade of research in New Guinea, says a new report from WWF.
- While the majority of 1,060 species listed are plants and insects, the inventory includes 134 amphibians, 71 fish, 43 reptiles, 12 mammals, and 2 birds.
- Among the most notable finds: a woolly giant rat, an endemic subspecies of the silky cuscus, a snub-fin dolphin, a turquoise and black ‘dragon’ or monitor lizard, and an 8-foot (2.5-m) river shark.
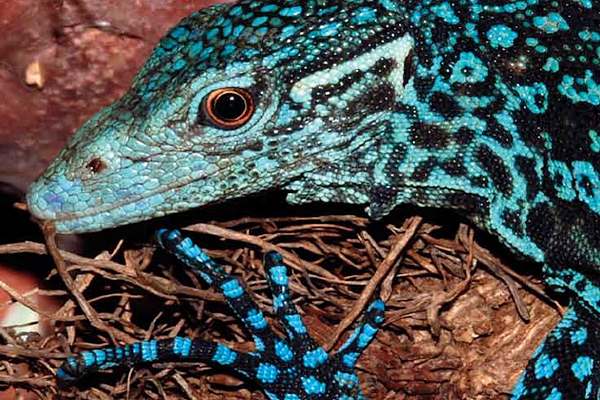

Varanus macraei monitor lizard © Lutz Obelgonner
Scientists discovered more than 1,000 previously unknown species during a decade of research in New Guinea (slideshow), says a new report from WWF.
Final Frontier: Newly Discovered species of New Guinea (1998 – 2008) (PDF-4.7MB) is a tally of 10 years’ worth of discoveries by scientists working on the world’s second largest island.
While the majority of 1,060 species listed are plants and insects, the inventory includes 134 amphibians, 71 fish, 43 reptiles, 12 mammals, and 2 birds.
Among the most notable finds: a woolly giant rat, an endemic subspecies of the silky cuscus, a snub-fin dolphin, a turquoise and black ‘dragon’ or monitor lizard, and an 8-foot (2.5-m) river shark.
 Final Frontier: Newly Discovered species of New Guinea (1998 – 2008)
|
 Litoria sauroni tree frog © Stephen Richards
|
WWF released the report to showcase New Guinea’s biodiversity, which includes more than 800 species of birds and more than 25,000 species of vascular plants in New Guinea ranges. New Guinea’s rainforests — the third largest after the Amazon and the Congo — and its coral reefs are astoundingly rich, yet still poorly studied relative to other places in the tropics. The dearth of information is a concern because New Guinea, which covers less than 0.5 percent of the Earth’s landmass, but is thought to be home to 6–8 percent of the world’s species, is facing an onslaught of threats from logging, large-scale industrial agriculture, and mining.
“This report shows that New Guinea’s forests and rivers are among the richest and most biodiverse in the world,” said Neil Stronach, WWF Western Melanesia’s Program Representative, in a statement. “But it also shows us that unchecked human demand can push even the wealthiest environments to bankruptcy.”
Ecosystems, especially forests, are threatened on both halves of New Guinea. On the western half — controlled by Indonesia — illegal logging is rampant and the government has granted, or is planning to grant, hundreds of thousands of hectares’ worth of forests for conversion to timber and oil palm plantations and large-scale rice and sugarcane operations. On the eastern part of the island, the Papua New Guinea government recently stripped communities of traditional land rights in favor of big business, especially foreign agricultural firms, which have been winning Special Agricultural and Business Leases (SABLs) to develop forest lands (a moratorium on SABLs was put in place last month). Meanwhile industrial logging has degraded large tracts of rainforest. Both sides of New Guinea have been affected by mining operations, which at times have caused pollution and exacerbated social conflict.
 Chilatherina alleni rainbowfish © Gerald R Allen
|
According to WWF, environmental degradation is already taking a toll in New Guinea, with the incidence of forest fires increasing, coastal erosion worsening, and depletion of forest resources for local use. Since 1972 a quarter of Papua New Guinea’s rainforests have been lost or degraded, while 99 of the island’s species are now listed on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, including 59 mammals, 34 birds and 6 frogs.
But WWF says there is still time to protect New Guinea’s flora, fauna, and incredible cultural richness (New Guinea is home to 15 percent of the world’s spoken languages). It highlights the potential to boost the capacity of local communities to use legal mechanisms to protect their lands and resources from expropriation and expresses optimism that the Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD) mechanism could generate revenue to support conservation activities (although the report fails to note the widespread corruption associated with early REDD efforts in Papua New Guinea). Final Frontier concludes by arguing that certification schemes for timber and agricultural commodities could help maintain New Guinea’s biodiversity in the future.
“It’s vital that New Guinea’s forests, rivers, lakes and seas are managed in a way that ensures they’ll continue to sustain economic and social development – and support the island’s fabulous wildlife,” states the report. “If we’re to safeguard this ‘final frontier’, it’ll require active partnerships between New Guinea’s communities and a wide range of stakeholders.”
 New Guinea Slideshow |