Brazil’s three largest supermarket chains, Wal-Mart, Carrefour and Pão de Açúcar, will suspend contracts with suppliers found to be involved in Amazon deforestation, reports O Globo.
The decision, announced at a meeting of the Brazilian Association of Supermarkets (Abras) this week, comes less than two weeks after Greenpeace’s exposé of the Amazon cattle industry. The report, titled Slaughtering the Amazon [], linked some of the world’s most prominent brands — including Nike, Toyota, Carrefour, Wal-Mart, and Johnson & Johnson, among dozens of others — to destruction of the Amazon rainforest for cattle pasture.
A statement from Abras said the association would develop guidelines and allow independent auditing to ensure that cattle products were not sourced from illegally cleared Amazon lands. Abras said the move is necessary because there is no “guarantee that the meat does not come from deforested areas in Amazonia.”
 Cattle and rainforest in the Brazilian Amazon. Photo by Rhett A. Butler |
The government has also responded to Greenpeace’s report. On the day that Slaughtering the Amazon was released, a Brazilian federal prosecutor filed a billion dollar law suit against the cattle industry for environmental damage. Firms that market tainted meat may be subject to fines of 500 reais ($260) per kilo.
Greenpeace welcomed the developments.
“This is an important first step towards winning a halt to further deforestation for cattle in the Amazon,” stated the NGO on its blog.
Cattle ranching is the biggest driver of deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon, accounting for roughly 80 percent of forest clearing. More than 38,600 square miles has been cleared for pasture since 1996, bringing the total area occupied by cattle ranches in the Brazilian Amazon to 214,000 square miles, an area larger than France. The legal Amazon, an region consisting of rainforests and a biologically-rich grassland known as cerrado, is now home to more than 80 million head of cattle, more than 85 percent of the total U.S. herd.
Related articles
Nike, Unilever, Burger King, IKEA may unwittingly contribute to Amazon destruction, says Greenpeace

(06/01/2009) Major international companies are unwittingly driving the deforestation of the Amazon rainforest through their purchases of leather, beef and other products supplied from the Brazil cattle industry, alleges a new report from Greenpeace. The report, Slaughtering the Amazon, is based on a three-year undercover investigation of the Brazilian cattle industry, which accounts for 80 percent of Amazon deforestation and roughly 14 percent of the world’s annual forest loss. Greenpeace found that Brazilian beef companies are important suppliers of raw materials used by leading global brands, including Adidas/Reebok, Nike, Carrefour, Eurostar, Unilever, Johnson & Johnson, Toyota, Honda, Gucci, Louis Vuitton, Prada, IKEA, Kraft, Tesco and Wal-Mart, among others.
Beef consumption fuels rainforest destruction
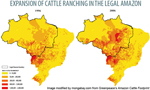
(02/16/2009) Nearly 80 percent of deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon results from cattle ranching, according to a new report by Greenpeace. The finding confirms what Amazon researchers have long known – that Brazil’s rise to become the world’s largest exporter of beef has come at the expense of Earth’s biggest rainforest. More than 38,600 square miles has been cleared for pasture since 1996, bringing the total area occupied by cattle ranches in the Brazilian Amazon to 214,000 square miles, an area larger than France. The legal Amazon, an region consisting of rainforests and a biologically-rich grassland known as cerrado, is now home to more than 80 million head of cattle. For comparison, the entire U.S. herd was 96 million in 2008.
Can cattle ranchers and soy farmers save the Amazon?

(06/06/2007) John Cain Carter, a Texas rancher who moved to the heart of the Amazon 11 years ago and founded what is perhaps the most innovative organization working in the Amazon, Alianca da Terra, believes the only way to save the Amazon is through the market. Carter says that by giving producers incentives to reduce their impact on the forest, the market can succeed where conservation efforts have failed. What is most remarkable about Alianca’s system is that it has the potential to be applied to any commodity anywhere in the world. That means palm oil in Borneo could be certified just as easily as sugar cane in Brazil or sheep in New Zealand. By addressing the supply chain, tracing agricultural products back to the specific fields where they were produced, the system offers perhaps the best market-based solution to combating deforestation. Combining these approaches with large-scale land conservation and scientific research offers what may be the best hope for saving the Amazon.














