World fertilizer prices surge 200% in 2007, hurting the poor
World fertilizer prices surge 200% in 2007
mongabay.com
February 20, 2008
The world’s poor lose as fertilizer price rise
|
|
World fertilizer prices surged by more than 200 percent in 2007, as farmers sought to maximize corn production for ethanol, according to the International Center for Soil Fertility and Agricultural Development (IFDC). Poor African farmers were hardest hit by the increase.
IFDC says the rise in fertilizer prices is fueled by new demand for grain for biofuel production, higher energy and freight prices, increased demand for grain-fed meat in emerging markets, and increased use of natural gas as liquefied natural gas (LNG).
“Farmers in industrialized countries are applying high levels of fertilizers to maximize harvests of grain at the highest prices ever,” said Dr. Balu Bumb, leader of the Policy, Trade, and Markets Program of IFDC. “Those forces drive fertilizer prices higher.”
IFDC notes that from January 2007 to January 2008 diammonium phosphate (DAP) prices rose from $252 per ton in January 2007 to $752 (U.S. Gulf price); prilled urea rose from $272 to $415 per ton (Arab Gulf price); and muriate of potash (MOP) rose from $172 to $352 (Vancouver price). At the same time the price of 1 metric ton of corn rose from $3.05/bushel to $4.28/bushel.
Bumb says the rise in prices is affecting poor farmers the most.
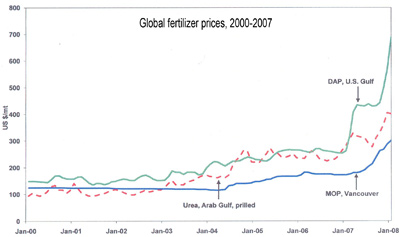 Monthly averages of fertilizer prices from 2000 to 2008. World fertilizer prices — especially diammonium phosphate — have skyrocketed during 2007. FOB = Free on board. Average price, with supplier paying freight and insurance, to destination port. DAP = diammonium phosphate. MOP = muriate of potash. Credit: Derived from Green Markets and FMB Weekly. Modified by mongabay.com |
“The unprecedented rise in fertilizer prices—more than 200% in the past year—is creating a fertilizer crisis for resource-poor farmers in developing countries,” Bumb says. “Particularly hard-hit are farmers in Sub-Saharan Africa. Farmers there need fertilizers desperately, to replenish their nutrient-depleted soils. But fertilizer use in Africa is the world’s lowest—about 8 kg per hectare. The lack of fertilizers in Africa accentuates hunger and poverty. To stimulate adequate fertilizer use, the purchasing power of the poorest of the poor must be enhanced through market-friendly safety nets so they can be included in the marketing process.”
The rising price of fertilizers contributes to a positive feedback loop for grain prices. As the cost of inputs increase, so do prices of food.
IFDC says the convergence of food prices and energy prices is fueling rocketing fertilizer prices.
“There was once a food economy and an energy economy—but the boom in biofuels is now merging the two,” said Phil Humphres, IFDC Senior Specialist-Engineering, noting that while 70 percent of corn production has traditionally been used as animal feed, the use of 18 percent to 20 percent of the 2007 U.S. corn crop was for ethanol, increased corn prices by 70 percent. He adds that the situation may worsen in 2008 when 25 percent of corn production is forecast to go into ethanol.
 Rice fields in Sulawesi, Indonesia. Photo by R. Butler. |
“In the United States, the government subsidizes ethanol by 51 cents a gallon [3.8 liters],” explained Humphres. “Large companies are contracting corn from farmers who apply more fertilizer to maximize production. But if all U.S. corn production were converted to ethanol, it would supply only 27% of the United States’ current transportation fuel demand.”
IFDC says changes in natural gas use are also influencing fertilizer prices. Gas that once went toward ammonia production in fertilizer manufacture is increasingly being liquefied (LNG) and used for energy.
The organization says that improvements in fertilizer use efficiency could help the current bottleneck.
“The sharp rise in fertilizer prices emphasizes the need for more research to improve the efficiency of fertilizer use,” said Dr. Amit Roy, IFDC President and Chief Executive Officer. “For example, most rice farmers in Asia broadcast urea directly into the floodwater. But only one bag in three is used by the plants. The rest is lost to the air and water.”
IFDC says it is working with farmers in developing countries to improve the efficiency of fertilizer use.
Related articles
UN: biofuels are starving the poor by driving up food prices
(2/14/2008) Echoing sentiments increasingly expressed by politicians, scientists, and advocates for the poor, the U.N. Food and Agriculture Organization warned that the world’s poorest people are suffering as a result of the push to use food crops for biofuel production.
Biofuels are worsening global warming
(2/7/2008) Converting native ecosystems for production of biofuel feed stocks is worsening the greenhouse gas emissions they are intended to mitigate, reports a pair of studies published in the journal Science. The studies follow a series of reports that have linked ethanol and biodiesel production to increased carbon dioxide emissions, destruction of biodiverse forest and savanna habitats, and water and air pollution.
U.S. biofuels policy drives deforestation in Indonesia, the Amazon
(1/17/2008) U.S. incentives for biofuel production are promoting deforestation in southeast Asia and the Amazon by driving up crop prices and displacing energy feedstock production, say researchers.
Global food prices rise 40% in 2007 to new record
(12/3/2008) As world food prices continue to surge, 37 countries are facing critical food crises due to conflict and disasters, according to a report from the U.N. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). FAO’s global food price index rose 40 percent this year to the highest level on record. Food costs in the world’s poorest countries — including Iraq, Afghanistan, Nepal, Pakistan, and 20 African countries — rose 25 percent to $107 billion.
Food prices to rise due to energy demand, economic trends
(12/3/2008)
Income growth, climate change, high energy prices, globalization, and urbanization are converging to drive food prices higher, threatening livelihoods and nutrition of poor people in developing countries, says a new report from the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI).