Humpback whale tracked migrating between ocean basins
.ongabay.com
August 18, 2005

Humpback Whale. Image courtesy of NOAA.
Background from Wikipedia.org:
The Humpback Whale (Megaptera novaeangliae) is a large whale (up to 50 feet [16m] long) found in oceans worldwide. The Humpback is well known its haunting whale song.
The Humpback Whale is a migratory species, spending its summers in cooler, high-latitude waters while mating and calving in tropical and sub-tropical waters. Annual migrations of up to 25,000 km (16,000 miles) are typical, making it one of the most well-travelled of any mammalian species.
Wildlife Conservation Society Release
Genetics links whale to two different ocean basins
Humpback likely born along Madagascar traveled to central Africa, says WCS researchers
August 18, 2005
For the first time ever, a genetic study has followed a single humpback whale from one ocean basin to another, adding to traditional notions of the migratory patterns of these majestic marine mammals in the process, according to researchers from the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS), the American Museum of Natural History (AMNH), and New York University. In the most recent Royal Society’s Biology Letters, a male humpback whale that was first sighted in Madagascar’s Antongil Bay in 2000 was found in 2002 swimming off the coast of Loango National Park in Gabon–on the other side of the African continent.
“While the movement of whales from one ocean to another has always been a possibility, it’s quite difficult to track in the wild,” said WCS researcher Dr. Cristina Pomilla, lead author of the study. “This study demonstrates the ability of molecular technologies to confirm the movements of an individual whale between ocean basins.”
The study examined DNA samples extracted from skin biopsies collected from whales in the wintering grounds of both the Indian and South Atlantic Oceans for evidence of inter-oceanic exchange of individuals. Using a method of genetic capture-recapture of genotypes constructed of microsatellite markers, the researchers identified an individual whale sampled in Gabonese waters in 2002 that had been first seen (and sampled) with its mother in Madagascar waters in 2000. Pomilla and her colleague, Dr. Howard Rosenbaum of WCS and AMNH, suspect that the whale could have been a three- to four-year old juvenile at the time of the second encounter with researchers.
The only other documentation of individual humpback whales moving from one ocean basin to another dates back to when the species still was hunted commercially. Two whales that were marked off western Australia (in the Indian Ocean basin) were later killed off the coast of eastern Australian, in the Pacific Ocean.
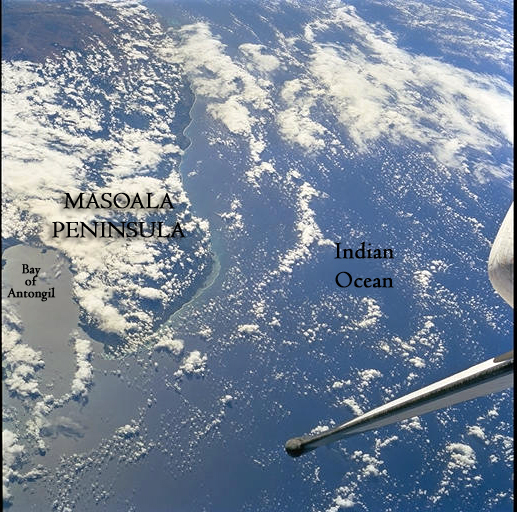
During breeding season, the Bay of Antongil in Madagascar is has one of the highest densities of humpback whales in the world. US-based nonprofit, the Wildlife Conservation Society, runs a research center on Nosy Mangabe and is currently working on the development of an Integrated Coastal Zone Management Plan for the bay. The best time to see the whales is July through September.
The identification of individual whales moving between ocean basins will help inform a number of conservation activities relating to humpback whales, including how these populations are defined, studied and managed. Humpback whales were hunted commercially until the International Whaling Commission protected the species globally in 1966.
“These findings will help us improve our understanding of how populations of whales are connected, both genetically and even culturally, in the form of the haunting songs that this species is well-known for,” added Rosenbaum. “In particular, inter-oceanic migration data will help us to better evaluate the current international management procedures for humpback whales.”
The is a WCS release.
