Where are the fish? Ocean fisheries in trouble
Meeting in Canada to discuss fate of global marine fisheries
mongabay.com
May 3, 2005
Talks began in Canada this week aimed at addressing the deteriorating condition of the world’s marine fisheries, but in an atmosphere with little reason for optimism. Past efforts to manage fisheries or control overfishing have largely failed to slow the depletion of marine resources.
Scientists, politicians, and fisherman alike know there’s a problem. Smaller fish and smaller catches suggest that the world’s oceans are no longer producing at their full potential. The bounty of the sea is becoming less generous — scientists estimate that the number of large fish in the oceans has fallen by as much as 90% since the 1950s. Improvements in technology have made it easier for fisherman to find and harvest more fish than ever before while demand for sea life products — which are consumed by both the rich and poor — is at an all time high.
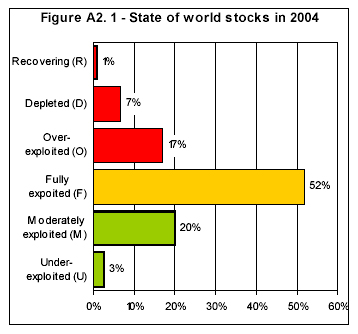 Table courtesy of the Marine Resources Service, Fishery Resources Division, FAO Fisheries Department. |
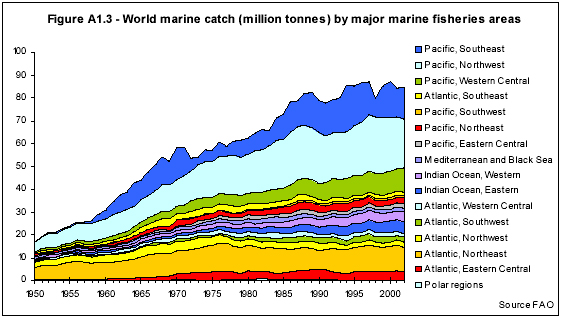
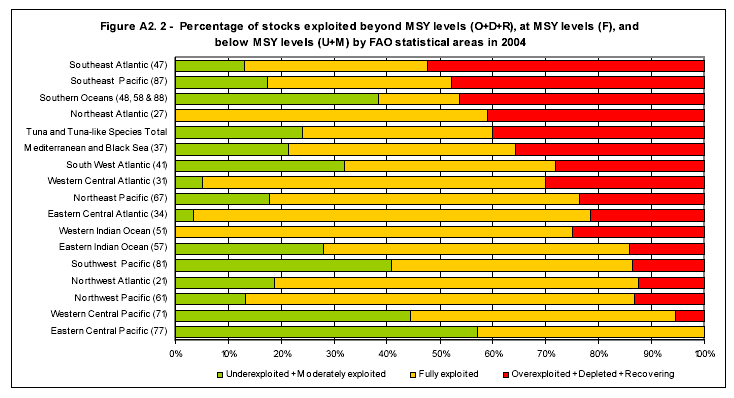
While global marine catches have yet to fall far from peak levels, a recent report (Review of the state of world marine fishery resources) from the The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization’s Fisheries Department says 77 percent of the world’s fish stocks are “fully exploited” — producing catches that are already at or very close to their maximum sustainable production limit, over-exploited, depleted, or recovering. The proportion of stocks FAO classifies as “under-exploited” has fallen to 3 percent, while the amount of “modertately exploited” stocks stands at 20 percent.
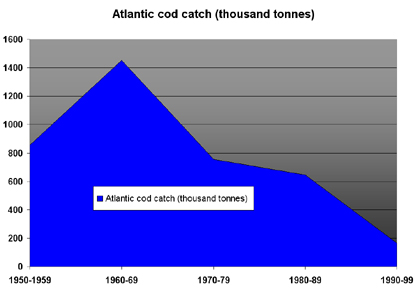 Chart showing decline of Atlantic cod catch off the coast of Newfoundland Graph based on data from the Marine Resources Service, Fishery Resources Division, FAO Fisheries Department. |
Several of the world’s important fisheries — including the cod and haddock fishery of the Grand Banks off Newfoundland in the north Atlantic — have collapsed and increasingly, fisherman are turning to smaller, less attractive, and less accessible species to make up for the shortfall of premium species. Trawlers are now fishing waters more than a mile deep to catch species such as the Orange roughy that few would have considered edible or useful a decade ago. These species are also at risk of overexploitation. In the case of the orange roughy, the southeast fishery of Australia saw its orange roughy catches fall from over 50,000 tonnes in 1990 to 5,579 tonnes in 1997.
Worse, the amount of waste in commercial fishing is staggering. More than 80 percent of catch in some fisheries may be by-catch, or species other than the species for which the fishing gear was set. Bycatch, also called incidental catch, is typically discarded at sea and may include fish, corals, sea turtles, and dolphins.
    Tables courtesy of the Marine Resources Service, Fishery Resources Division, FAO Fisheries Department. |
Fishermen race for fish
The fundamental problem with facing the management of the world’s fisheries is the “tragedy of the commons.” Since in many areas, ocean fish are essentially an open access resource there is no incentive for an individual fisherman to restrain his catch. If an individual fisherman conserves for tomorrow, he is only providing someone else with the resource today.
Looking for a solution
Assigning property rights may help the situation and in some areas such schemes have showed signs of success. On the open ocean however, it is considerably more difficult to enforce boundaries and set binding fishing limits. Plus, there is no guarantee that local fisheries will not be overexploited by commercial interests. As some wealth countries have depleted their own fisheries, they have moved into poor countries, buying fishing rights — often from corrupt bureaucrats — and then continuing their unsustaiable plunder of marine resources.
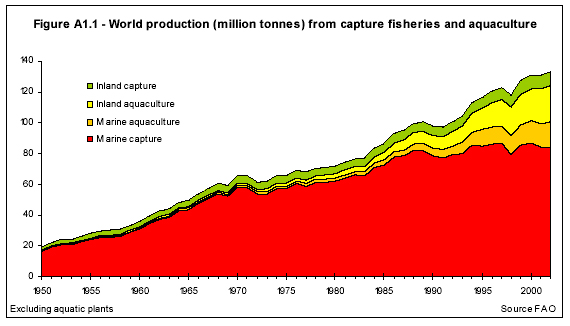
Some have argued that a global network of marine parks could help protect and restore some of the world’s most impacted fisheries, while aquaculture — which has expereinced tremendous growth in recent years — could supplement protein needs. But in order for any sort of conservation plan to be successful, all the involved parties must be brought to the table to hammer out a mutually agreeable plan. If past summits are any indication, this could take a very long time.
Current state of exploitation of selected species and groups
fished in the Northwest Atlantic (Adapted from FAO Fisheries Department data 2004).
| Stock or species groups | Scientific name | Main fishing countries in 2002 | State of exploitation* |
| Amer. plaice(=Long rough dab) | Hippoglossoides platessoides | Canada, USA, Spain, Portugal | F |
| Flatfishes nei | Pleuronectiformes | Canada, Portugal | F |
| Greenland halibut | Reinhardtius hippoglossoides | Greenland, Spain, Canada, Russian Fed | F |
| Summer flounder | Paralichthys dentatus | USA | F |
| Winter flounder | Pseudopleuronectes americanus | USA, Canada | F |
| Witch flounder | Glyptocephalus cynoglossus | USA, Canada, Spain, Portugal | F |
| Yellowtail flounder | Limanda ferruginea | Canada, USA | F |
| Other Flounders, halibuts, soles | F | ||
| Flounders, halibuts, soles | |||
| Atlantic cod | Gadus morhua | Canada, USA, Greenland | D |
| Haddock | Melanogrammus aeglefinus | Canada, USA | D |
| Saithe(=Pollock) | Pollachius virens | Canada, USA | F |
| Silver hake | Merluccius bilinearis | Canada, USA, Russian Fed | U |
| Tusk(=Cusk) | Brosme brosme | Canada, USA | F |
| White hake | Urophycis tenuis | Canada, USA, Spain, Portugal | F |
| Other Cods, hakes, haddocks, etc. | F | ||
| Cods, hakes, haddocks, etc. | |||
| Miscellaneous costal fishes | ? | ||
| American angler | Lophius americanus | USA, Canada | F |
| Atlantic redfishes nei | Sebastes spp | Russian Fed, Canada, Lithuania, Portugal | F |
| Other Miscellaneous demersal fishes | ? | ||
| Miscellaneous demersal fishes | |||
| Atlantic herring | Clupea harengus | Canada, USA | U-F-R |
| Atlantic menhaden | Brevoortia tyrannus | USA | F |
| Other Herrings, sardines, anchovies | ? | ||
| Herrings, sardines, anchovies | |||
| Atlantic mackerel | Scomber scombrus | Canada, USA | F |
| Capelin | Mallotus villosus | Canada | F |
| Other Miscellaneous pelagic fishes | U | ||
| Miscellaneous pelagic fishes | |||
| American lobster | Homarus americanus | Canada, USA | F/O |
| Lobsters, spinyrock lobsters | |||
| Pandalus shrimps nei | Pandalus spp | Canada | F |
| Other Shrimps, prawns, etc. | ? | ||
| Shrimps, prawns, etc. | |||
| American sea scallop | Placopecten magellanicus | USA, Canada | M-F |
| Atlantic bay scallop | Argopecten irradians | USA | ? |
| Iceland scallop | Chlamys islandica | Greenland, Canada | |
| Scallops, penctens, etc. | |||
| Atlantic surf clam | Spisula solidissima | USA | M-F |
| Northern quahog(=Hard clam) | Mercenaria mercenaria | USA, Canada | M-F |
| Ocean quahog | Arctica islandica | USA | M-F |
| Sand gaper | Mya arenaria | USA, Canada | ? |
| Other Clams, cockles, arkshells, etc. | ? | ||
| Clams, cockles, arkshells, etc. | |||
* (U) Underexploited; (M) Moderately exploited; (F) Fully exploited; (O) Overexploited; (D) Depleted; (R) Recovering.
You can learn more on the state of the world’s fisheries at http://www.fao.org/fi/default.asp